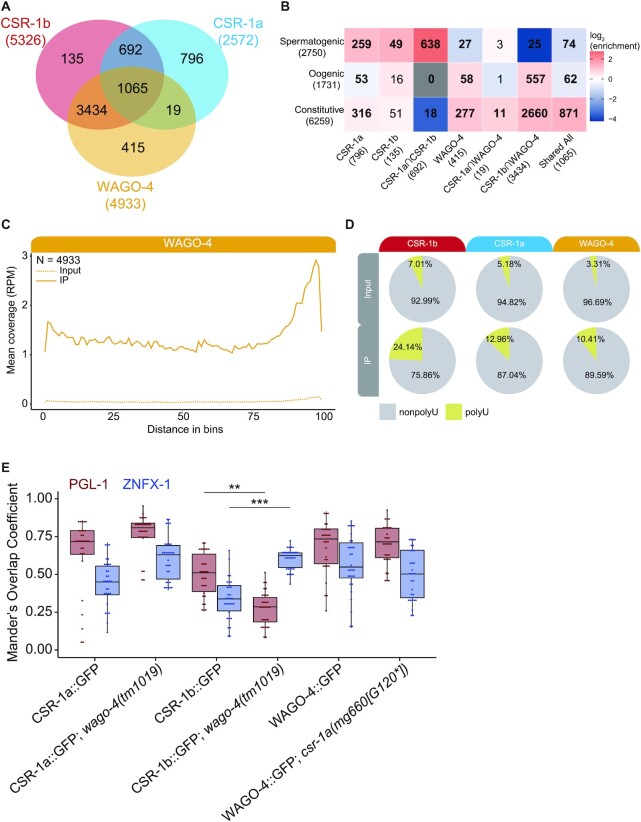
Figure 8.
CSR-1 isoforms intersect differently with the WAGO-4 22G-RNA pathway. (A) Venn diagram showing the overlap between CSR-1a/b 22G-RNA targets and WAGO-4 22G-RNA targets from L4 AGO IP samples. (B) Heatmap depicting the overlap between 22G-RNA protein coding targets of CSR-1b only, CSR-1a only, WAGO-4 only, and various shared target groups with mutually exclusive germline constitutive, oogenic, and spermatogenic enriched transcript sets (29). Bold numbers indicate significant enrichment in overlapping genes (Fisher's Exact Test, P< 0.05). Enrichment = number of overlapping genes divided by the expected number of overlapping genes drawn from two independent groups. (C) Metagene plot of the distribution of WAGO-4 enriched 22G-RNAs antisense to protein coding genes along the gene body. N = Number of genes. (D) Pie charts of percentage of total reads with U-tailing (chartreuse; addition of one or more non-templated uridines) for Input (top) and IP (bottom) samples of CSR-1b, CSR-1a, and WAGO-4 sRNAs (all genome matching sRNAs are included) (E) Quantification of the number of GFP::3xFLAG::CSR-1a, GFP::3xFLAG::CSR-1b, and WAGO-4::GFP pixels that overlap with PGL-1::mRFP (burgundy) or HA::TagRFP::ZNFX-1 (blue) pixels in wild-type or mutant worms, using Mander's Correlation. For each data set, five Z stacks of proximal germline regions from six different animals per strain were counted (N = 30 slices, approximately 80–100 nuclei per worm). Significance was analyzed as a mixed-effects ANOVA. ** indicates significance of P< 0.01, *** indicates significance of P< 0.001.