Figure 3.
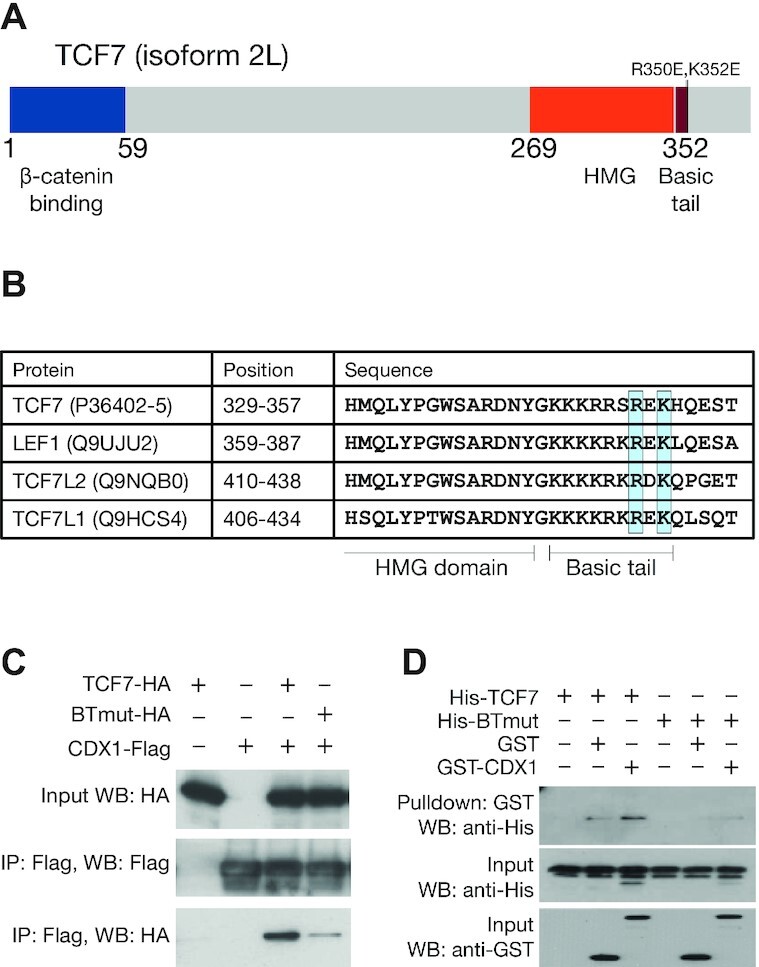
TCFs bind to CDX proteins through highly conserved residues in the basic tail. (A) Cartoon of TCF7 protein with functional domains highlighted. Positions of R350E and K352E, mutations which interfere with the TCF–CDX interaction, are highlighted. (B) Alignment of the C-terminal portion of the HMG domain and basic tail of the 4 human TCFs showing conservation of R350 and K352. Uniprot identifiers for the proteins are shown along with positions of the residues in the alignment. (C) Co-IP showing that the BTmut variant of TCF7 with 2 amino acid substitutions (R350E,K352E) shows attenuated binding to CDX1. HEK293T cells were transfected with CDX1-flag and HA-tagged WT or BTmut variants of TCF7. Cell lysates were subjected to an anti-Flag IP and examined using anti-HA and anti-Flag western blots (WB). Input samples were used as loading control. (D) GST pulldown showing direct binding between recombinant CDX1 and WT TCF7 but not BTmut. Purified His-tagged TCF7 or BTmut proteins were pulled down using glutathione beads with GST or GST-tagged CDX1 as bait. Precipitates were analysed on an anti-His WB.
