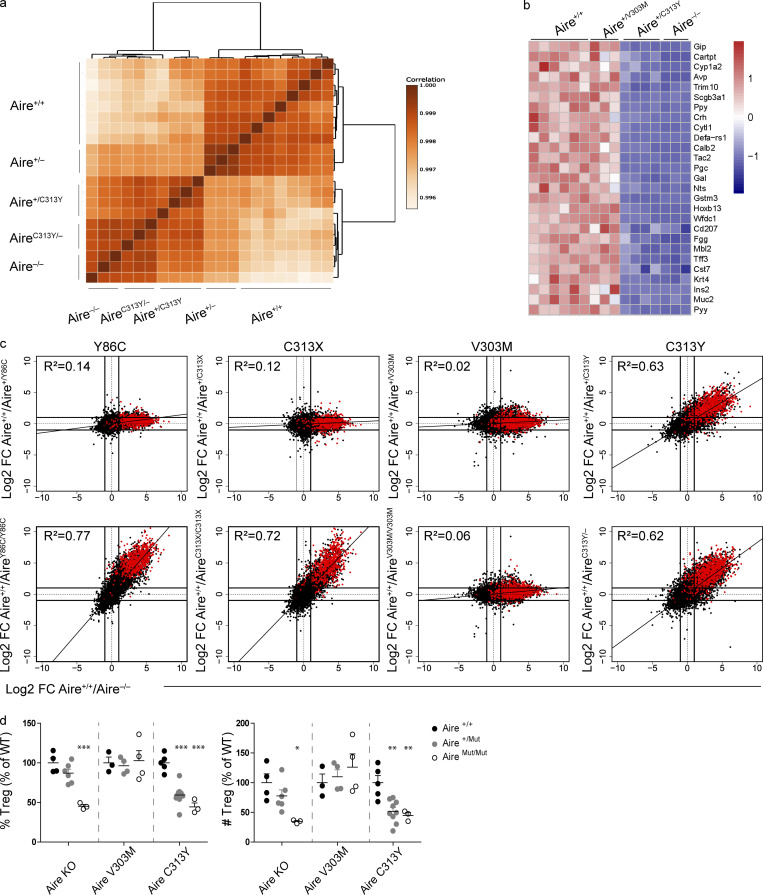
Figure 2.
Heterozygous Aire+/C313Y mutation, but not Aire+/V303M, impairs ectopic expression of AIRE target genes in mTECs and the thymic T reg cell compartment. (a) Dendrogram and heatmap of Pearson correlation coefficient between the different mTEChi bulk RNAseq samples based on gene expression values. (b) Heatmap of normalized read counts of 27 representative AIRE-dependent genes in mTEChi of NOD.Aire+/+, NOD.Aire+/V303M, NOD.Aire+/C313Y, and NOD.Aire−/−. Expression is normalized per row. (c) FC/FC plots of mTEChi gene expression comparing WT/heterozygous AIRE mutants (top, y axis) to Aire+/+/Aire−/− (x axis) of the same background or WT/homozygous AIRE mutants (bottom, y axis) to Aire+/+/Aire−/− (x axis) of the same background. All genes are depicted by black dots along with a trendline for the best linear fit, and R2 is indicated in each plot. A signature of AIRE-dependent TRA genes, which are down-regulated by at least 10-fold in B6.Aire−/− (based on a dataset from Sansom et al., 2014) is superimposed using red dots. All animals within a strain are littermates. (d) Frequency (left) and absolute counts of T reg cells (right; CD4+CD8–CD25+Foxp3+) in thymi of different NOD AIRE mutants created in this study, as well as Aire−/− on a NOD background. Data from three to nine mice per group, analyzed by one-way ANOVA, are represented as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 from the relevant WT littermate control. Both frequencies and absolute counts are calculated as a percentage from the average frequency or count of all WT animals within a given experiment. Each mouse strain was evaluated separately. At least two independent experiments were conducted on each strain.