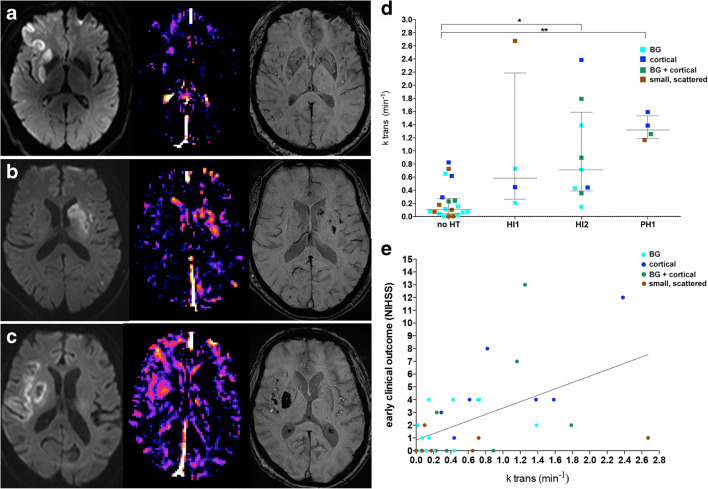
Fig. 2.
Permeability signatures and their correlation to hemorrhagic transformation illustrated in combined basal ganglia and cortical infarcts. Diffusion-weighted images, ktrans maps, and susceptibility-weighted images of three representative patients are displayed. In the first row, diffusion restriction in the right striatum and adjacent cortex is seen with focal ktrans increase in the right striatum, but no hemorrhagic transformation (a). In the second row, diffusion restriction in the left BG and a small portion of the insular cortex as well as in the temporal cortex is evident. Diffusion restriction co-localizes with increased ktrans and hemorrhagic infarction type 2 in the caudate head in the striatum and the insular cortex. (b) In the third row, diffusion restriction is seen in the right striatum and the adjacent cortex with increased ktrans and parenchymal hemorrhage type 1 in the striatum as well as petechial hemorrhages in the insular cortex (c). Patients without hemorrhagic transformation displayed a significantly lower ktrans compared to patients with hemorrhagic infarction type 2 or parenchymal hemorrhage type 1 (d). A moderate correlation of early clinical outcome and ktrans values was apparent (e)