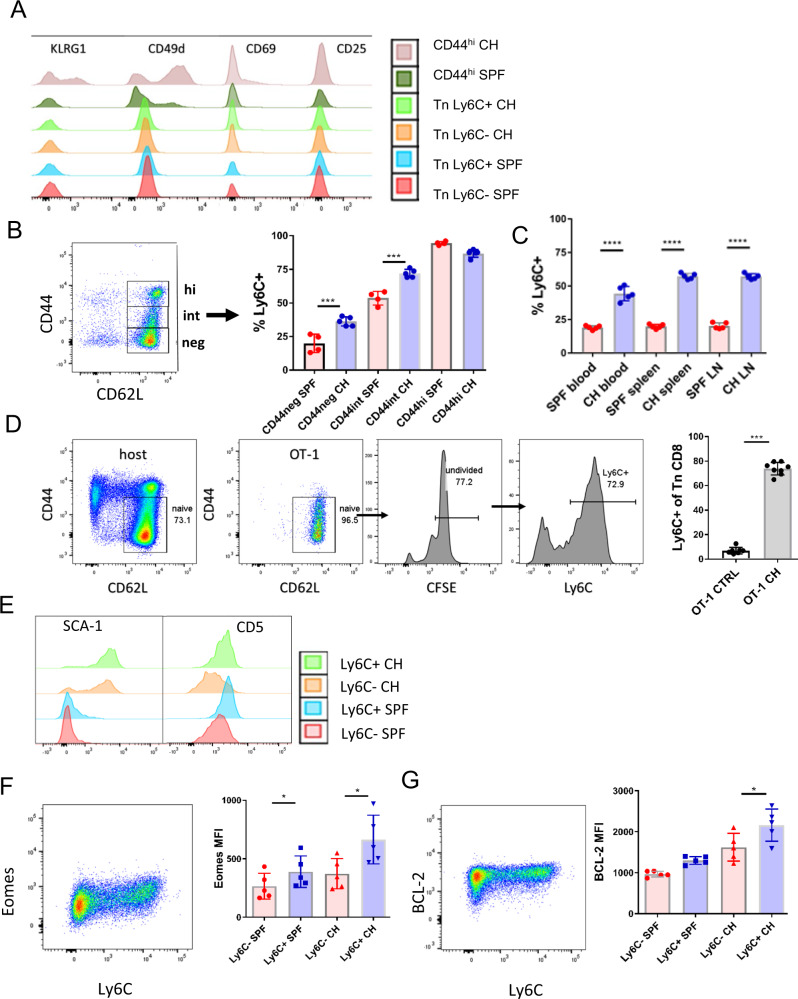
Fig. 4. Microbial colonization increases Ly6C expression on CD8+ Tn cells in a bystander manner.
A Female C57BL/6 mice were cohoused with outbred, wild-type pet shop mice in large rat cages, separated by a perforated barrier. After >60 days of cohousing expression of Cd49d, CD69, KLRG1, CD27, and CD25 was analyzed by flow cytometry on subpopulations of Tn CD8+ T cells from lymph nodes of CH mice and SPF controls (Color scheme: red-Tn Ly6C− from SPF mice; blue-Tn Ly6C+ from SPF mice; orange-Tn Ly6C− from CH mice; light green-Tn Ly6C+ from CH mice; dark green-CD44hi from SPF mice; brown-CD44hi from CH mice). B Upregulation of Ly6C was upregulated on central memory (CM) cytotoxic T cells (CD8+CD44hiCD62Lhi), CD44negCD62Lhi and CD44intCD62Lhi cells (n = 4 SPF mice, n = 5 CH mice per group, data presented as mean ± sd, ***p < 0.001). C Ly6C was upregulated on Tn CD8+ cells in the blood, lymph nodes, and spleen (n = 5 mice per group, data presented as mean ± sd, ****p < 0.0001). D Tn CD8+ cells were magnetically enriched, CFSE labeled and transferred into CH mice for 14 days (n = 7 ctrl mice, n = 8 CH mice, data presented as mean ± sd, ***p = 0.0003). E Expression of CD5 and SCA-1 on Ly6C ± CD8+ Tn from SPF and CH (Color scheme: red-Tn Ly6C− from SPF mice; blue-Tn Ly6C+ from SPF mice; orange-Tn Ly6C− from CH mice; light green-Tn Ly6C+ from CH mice). F Ly6C ± CD8+ Tn from SPF and CH (n = 5 mice per group, data presented as mean ± sd, left to right *p = 0.0481, *p = 0.0336) were stained intracellularly for expression of Eomes and (G) BCL-2 (n = 5 mice per group, data presented as mean ± sd, *p = 0.0168). A, B, C, E, F, and G data are representative of two experiments (with n = 5 mice per group). D Data are pooled from two experiments (total N = 7 mice per group (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). D Two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-test; A, B, C, E, F, and G) one-way ANOVA, with Sidak post hoc correction.