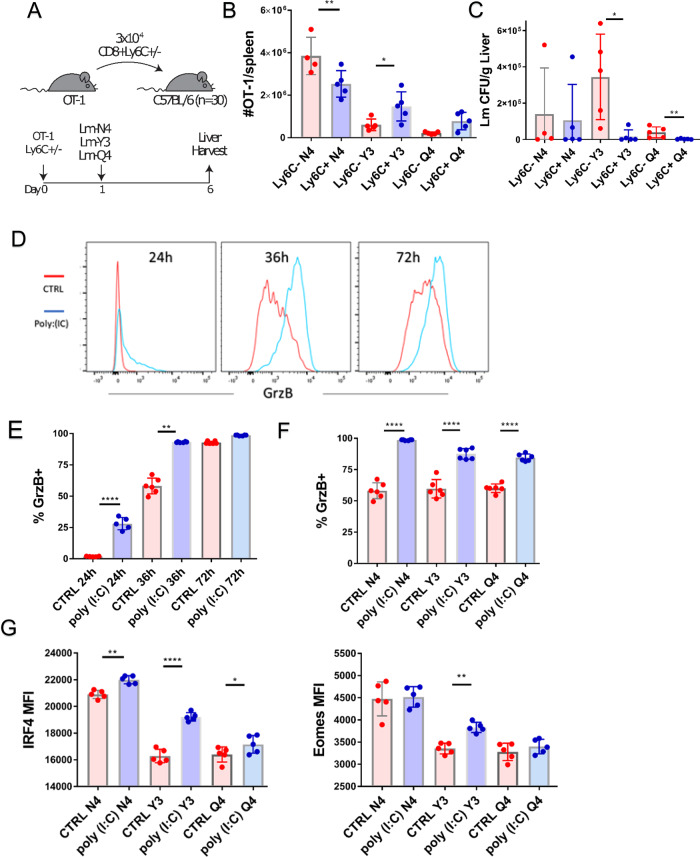
Fig. 9. Ly6C+ naïve CD8+ T cells show enhanced effector function against low-affinity alternative peptide ligands.
A Mice were inoculated i.v. with ~104 CFU Lm genetically engineered to express the native immunodominant CD8+ ovalbumin peptide SIINFEKL (N4) or its two altered peptide ligands (APLs) Y3 and Q4. Twenty-four hours later we transferred 3 × 104 sorted Ly6C± cells from OT-1 mice into total 6 groups of mice (n = 5 mice per group) (transfer scheme). B On day 5 post-transfer the number of GzB-producing donor cells in the spleen and liver (n = 5 mice per group, data presented as mean ± sd, *p = 0.0372, **p = 0.0029). C Host bacterial burdens in the liver were measured for every Lm APL administered (n = 5 mice per group, data presented as mean ± sd, *p = 0.0159, **p = 0.0079). D, E Tn CD8+s were magnetically enriched from control and poly(I:C) treated mice (Color scheme: red-control mice; blue-poly(I:C) treated mice) and stimulated in vitro with 10−7 M SIINFEKL peptide and Y3 and Q4 APLs. Production of GzB was measured at 24 h (n = 5 mice), 36 and 72 h of stimulation (n = 6 mice, data presented as mean ± sd, *p = 0.0022, ****p < 0.0001) F At 36 h GzB expression was higher in cells from mice pretreated with poly(I:C) when stimulated with any of the three peptides (n = 6 mice, data presented as mean ± sd). G At the same time point expression of transcription factors Eomes and IRF4 was increased in poly(I:C) pretreated cells (n = 5 mice, data presented as mean ± sd, *p = 0.0491, **p = 0.0031, ****p < 0.0001). A–G Data are representative of two independent experiments (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001). B p values calculated by unpaired Students t-test between mice groups receiving same APL, C Mann-Whitney U test between mice groups receiving same APL E, F, G Students t-test.