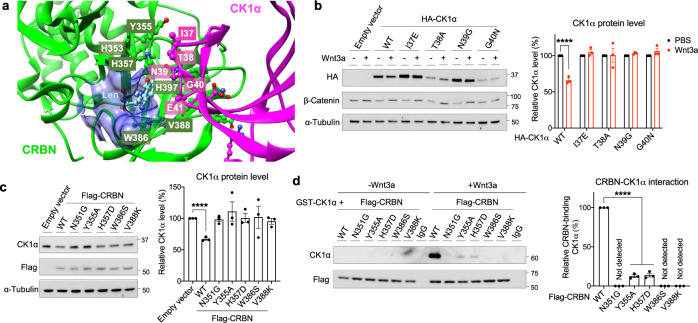
Fig. 4. Wnt signaling induced CRBN-mediated degradation of CK1α requires its IMiD binding pocket.
a A structural model of CRBN-lenalidomide-CK1α complex (PDB: 5fqd). The interacting residues at the interface of the CRBN (green with white text) and CK1α (magenta with white text) are shown as a ball and stick model. The IMiD binding pocket is depicted in blue. b HEK cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding wild-type (WT) HA-tagged CK1α or an HA-tagged CK1α mutant, followed by PBS or Wnt3a treatment for 24 h. Extracts of these cells were evaluated by immunoblotting. A representative immunoblot (left panel) and a quantification of immunoblots (mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments; right panel) are shown. c HEK cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding WT Flag-tagged CRBN or the indicated Flag-tagged CRBN mutants. Extracts of these cells were evaluated by immunoblotting. A representative immunoblot (left panel) and a quantification of immunoblots (mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments; right panel) are shown. d HEK cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding WT Flag-tagged CRBN the indicated Flag-tagged CRBN mutants and subsequently treated with PBS or Wnt3a for 4 h. Flag-CRBN immunoprecipitated from extracts of these cells were incubated with the indicated amounts of recombinant GST-CK1α at 4 °C for 1 h. Flag-CRBN beads were re-isolated, washed, and CK1α bound was eluted using sample buffer. These immunoprecipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting. IgG beads serve as a control for Flag-CRBN beads. A representative immunoblot (left panel) and a quantification of immunoblots (mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments; right panel) are shown. Asterisks in b–d indicate statistical significance (two-tailed Student’s t-test, *p value < 0.05, ****p value < 0.0001).