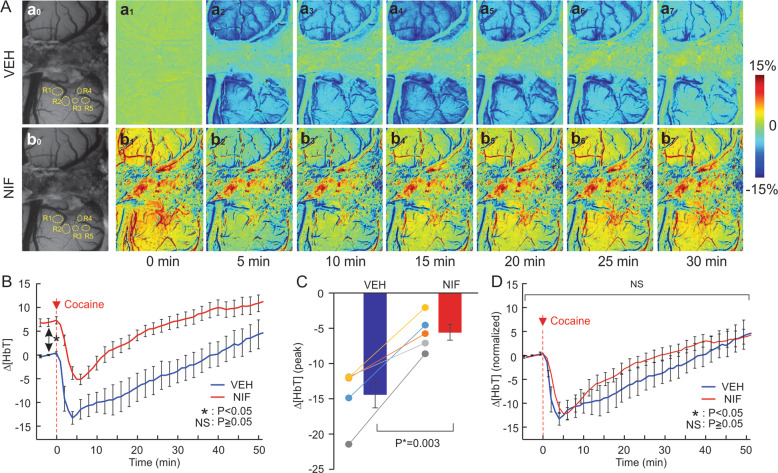
Fig. 3. Pretreatment of NIF increased blood volume and attenuated its absolute but not its relative reduction.
A Representative images of the dynamic changes in cerebral blood volume (∆[HbT]) in response to cocaine (1 mg/kg, i.v.) in PFCs after vehicle (VEH, upper panel) and NIF-pretreatment (NIF, lower panel); Panels Aa0 and Ab0 show representative images for baseline before and after NIF (0.5 mg/kg, i.v.), respectively. B Dynamic measures of cocaine-induced cerebral blood volume (∆[HbT]) changes with vehicle and with NIF pretreatment (0.5 mg/kg, i.v.). C Comparison of the integrated decreases in ΔHbT (n = 5) between vehicle and NIF pretreatment after cocaine. D Normalized dynamic change in (∆[HbT]) following cocaine at time t = 0 min. These results show that NIF pretreatment (0.5 mg/kg, i.v.) dilates vessels, elevating baseline cerebral blood volume and attenuated the non-normalized cocaine-induced (∆[HbT]) decreases. Values in graphs correspond to mean and standard errors. ROIs: the regions of interest. For a given animal these ROIs were placed in the same location in hemodynamic channels to the Ca2+ fluorescence channel. *p < 0.05; NS: not significant.