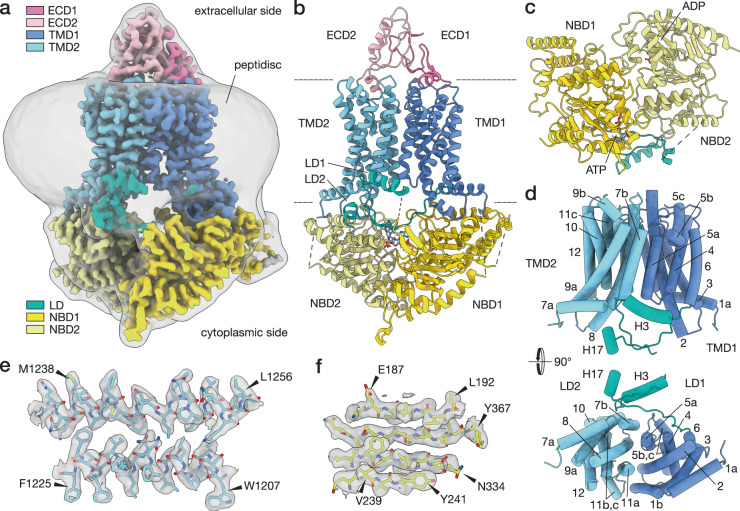
Fig. 1. Structural features of Pdr5.
a Depicted here is the cryo-EM map of Pdr5 in inward-open conformation (ADP-Pdr5). The map is coloured according to the domain organisation (see key). The grey transparent envelope surrounding the protein is a Gaussian-filtered (2σ) version of the same map, showing the extent and shape of the peptidisc shell around Pdr5. b Atomic model of Pdr5 built and refined against the map, in cartoon representation. c Top view (cytoplasmic side) of the nucleotide-binding domains of Pdr5, showing the position of the bound nucleotides. The linker domain is also depicted. d Side and top views of the transmembrane domain of Pdr5 with α-helices shown schematically as cylinders and numbered sequentially (TH1a–12) from the N-terminus (cf. Supplementary Fig. 5 and S6). This panel also includes the linker domain and its two helices H3 and H17. e, f Two portions of the ADP-Pdr5 cryo-EM map, showing the reconstructed volume around representative secondary structural features: e α-helices TH7b and TH8 of TMD1 domain and (f) a β-sheet in NBD1 domain. Arrowheads point to amino acid residues that have been arbitrarily chosen for orientation purposes. Abbreviations: ECD, extracellular domain; LD, linker domain; NBD, nucleotide-binding domain; TMD, transmembrane domain.