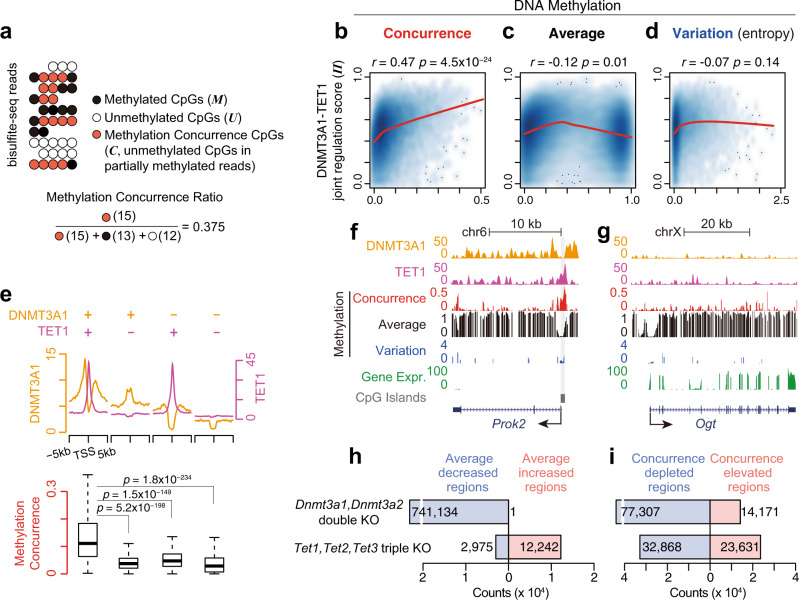
Fig. 1. The methylation concurrence ratio measures the antagonism between methylation and demethylation processes in mESCs.
a Schematic of DNA methylation concurrence captured by bisulfite-seq. Solid circles are methylated cytosines. Blank circles are unmethylated cytosines. Red circles are unmethylated cytosines in partially methylated reads, i.e., methylation- concurrence cytosines. The equation below shows the calculation of methylation concurrence ratio using the example above. b Methylation concurrence is positively correlated with the ‘DNMT3A1-TET1 joint regulation score’ (Π) in gene promoter regions. Average methylation (c) and methylation variation (d) are not correlated with Π at gene promoters. Spearman’s rank correlation was calculated. P values were calculated by the two-tailed correlation test for Spearman’s correlation. LOWESS lines were plotted to describe the relationships between variables (indicated by red curves). e The methylation concurrence ratio is significantly higher at DNMT3A1&TET1 co-occupied promoters. Gene numbers of each groups: ‘DNMT3A1 + TET1+’, n = 1294; ‘DNMT3A1 + TET1 − ’, n = 1238; ‘DNMT3A1−;TET1+’, n = 1370; ‘DNMT3A1 − TET1 − ’, n = 1595. The two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test was used for the significance test. The line in the box center refers to the median, the limits of box refer to the 25th and 75th percentiles and whiskers are plotted at the highest and lowest points within the 1.5 times interquartile range. f UCSC Genome Browser tracks show DNMT3A1 binding (orange), TET1 binding (purple), methylation concurrence (red), average methylation (black), methylation variation (blue), and gene expression data (green) at Prok2 gene. CpG islands are shown in gray. g Same as (f), but for gene Ogt. h Dnmt3a knockout leads to a decrease in average methylation, while Tet knockout leads to hypermethylation. i Both Dnmt3a knockout and Tet knockout lead to more concurrence depletion than elevation. According to the original paper, the ‘Dnmt3a1, Dnmt3a2 double knockout’ sample is generated by reintroducing DNMT3B1 into stem cells that lack DNA methylation due to deletions of all Dnmt genes (Dnmt3a1, Dnmt3a2, and Dnmt3b1). The genomic binding of the reintroduced DNMT3B1 in knockout cells resembles that in wild-type ES cells22.