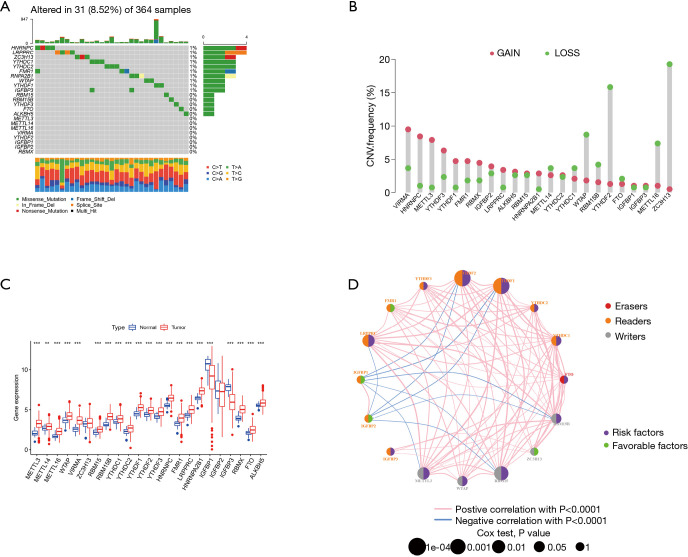
Figure 1.
Genetic alteration of the m6A modulation gene in HCC. (A) In all, 31 of 364 HCC patients experienced modulations of 23 m6A genetic alterations with a frequency of 8.52%. These alterations mainly included missense mutation, splice site mutation, and nonsense mutation. (B) CNV mutation frequency of the 23 m6A regulatory genes. This column represents the frequency of change. Deletion frequency is represented by green dots, while amplification frequency is represented by pink dots. (C) Expression of the 23 m6A regulatory genes in normal tissues and HCC tissues. (D) Expression interaction of the 23 m6A regulatory genes in HCC. The lines connecting the m6A regulatory genes show how they are correlated with each other, with positive associations in red and negative associations in blue. The size of each circle represents the prognostic effect of each regulatory gene and is scaled by P value. The color of the circle’s left half represents the modification type of m6A (erasers, readers, writers), while the circle’s right half represents survival factors affecting the patients. Green represents protective factors, and purple represents risk factors. m6A, N6-methyladenosine; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; CNV, copy number variation.