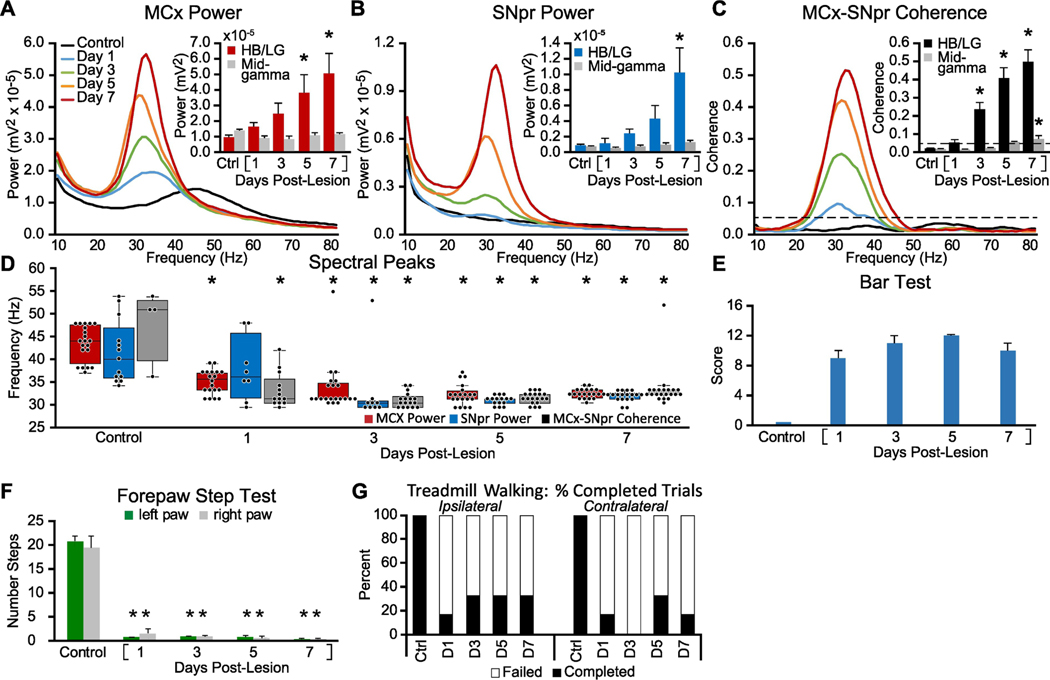
Figure 2: Alterations in MCx and SNpr high beta/low gamma LFP activity, LFP spectral peaks, and motor performance in the week following bilateral 6-OHDA induced dopamine cell lesion.
Recordings were obtained before (Control/Ctrl) and after bilateral DA-cell lesion on days 1, 3, 5, and 7 during epochs of intermittent walking in an open cylinder rotating at a reduced speed (5 RPM vs. 9 RPM, see methods). A-C: Averaged MCx and SNpr LFP power spectra and MCx-SNpr coherence spectra with bar graphs (inset) depicting mean total LFP power around dominant peaks in the HB/LG frequency range in the MCx (D, red bars), SNpr (E, blue bars) and MCx-SNpr coherence (F, black bars), and in the mid-gamma range (D-F grey bars). Bar graphs show linear increases in MCx (R2 = 0.98), and SNpr (R2 = 0.97) HB/LG oscillatory activity and MCx-SNpr coherence (R2 = 0.96) following the 6-OHDA injection relative to control (Ctrl). * p < 0.05, relative to control. D: Dominant spectral peaks in MCx and SNpr LFP power and MCx-SNpr coherence spectra in recordings from before and after bilateral 6-OHDAmediated dopamine cell lesion during treadmill walking. Box plots depict 25th to 75th percentile values and black dots show individual peak frequencies in the 29 – 55 Hz range. * p < 0.05, relative to control. E-G: Motor function in control rats and following bilateral DA cell lesion. E: Bar graph shows stable catalepsy starting from day 1 post-lesion (2 rats). F: Bar graph shows number of steps made by the right and left paws in the forelimb step test during control and post-lesion days compared to control. G: Bar graph indicates the % completed trials (black bars) vs incidences of failure (white bars) to initiate and maintain steady treadmill walking for at least 30 seconds when oriented in the direction contralateral to the lesion. * p < 0.05, relative to control, n = 3 rats.