Fig. 2. SLC7A5-dependent late endosomal mTORC1 activation in naïve CD4+ T cell responses.
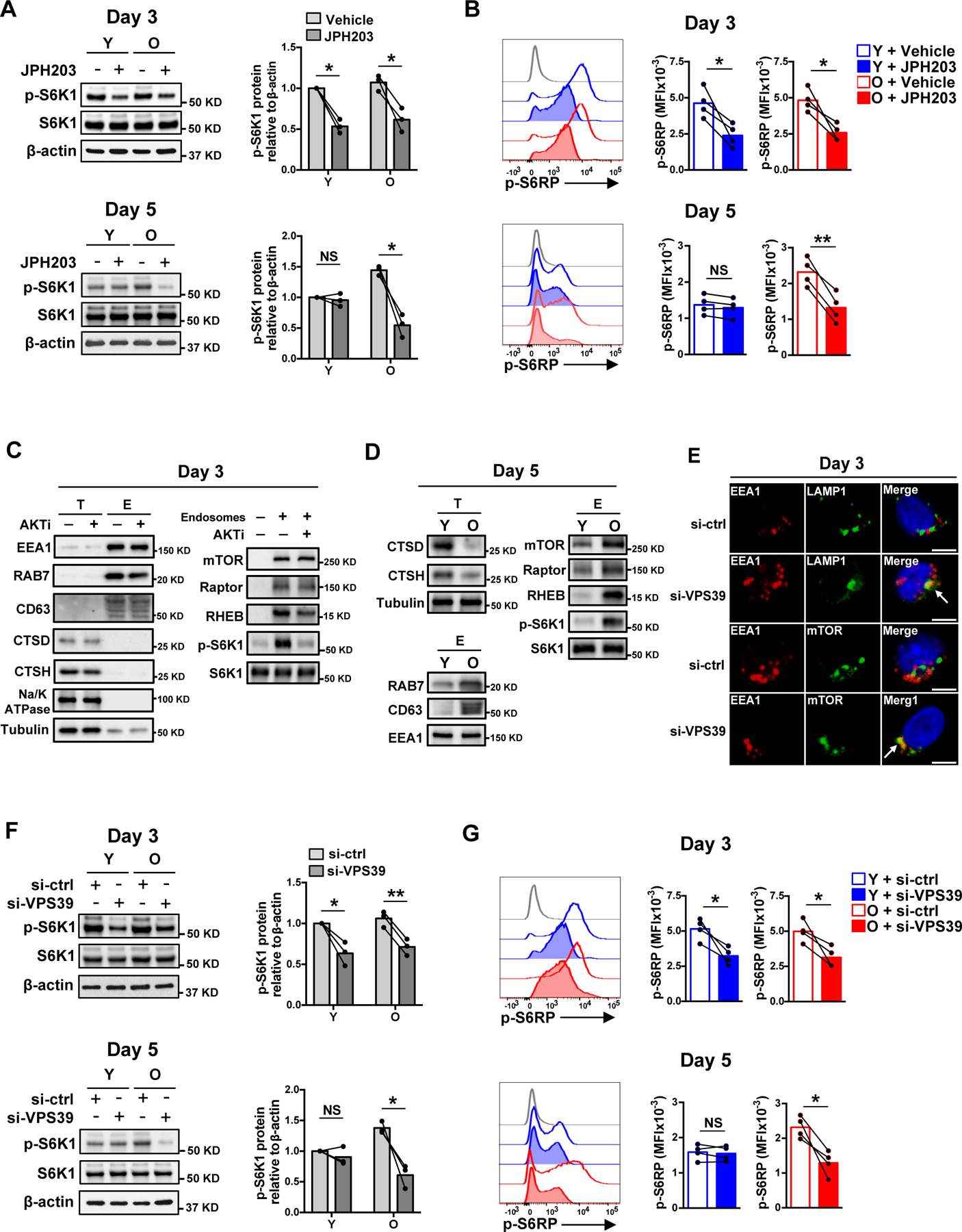
(A and B) Naïve CD4+ T cells from young and older healthy individual were activated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads for 3 days in the presence of vehicle or SLC7A5 inhibitor JPH203 (upper panel). Alternatively, cells were activated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads for 5 days with the last 2 days in the presence of vehicle or JPH203 (lower panel). mTORC1 activities were determined either by Western blotting of p-S6K1 (A) or by flow cytometry of intracellular p-S6RP (S235/S236) (B). Data are shown as one representative experiment (left) and cumulative data of three or four experiments (right). (C) Naïve CD4+ T cells were activated for 3 days followed by treatment or not with an AKT inhibitor for 2 hours prior to harvesting. Endosomes were isolated and analyzed for in vitro mTORC1 kinase activity toward S6K1. Total cell lysates (T) and endosome isolates (E) were analyzed by immunoblotting for indicated proteins. Data are shown as one representative of three experiments. (D) In vitro mTORC1 kinase activity of endosome isolates in day 5-stimulated naïve CD4+ T cells from one young and one older individual. Data are shown as one representative of three experiments. (E) Cells were stained with anti-EEA1, anti-LAMP1 and anti-mTOR. Confocal images representative of two independent experiments are shown. Scale bar, 5 μm. (F and G) mTORC1 activities in day 3- and day 5-stimulated naïve CD4+ T cells from young and older individuals after control or VPS39 silencing. The gray histogram represents isotype control. Comparison by two-tailed paired t test (A, B, F and G). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; NS, not significant.
