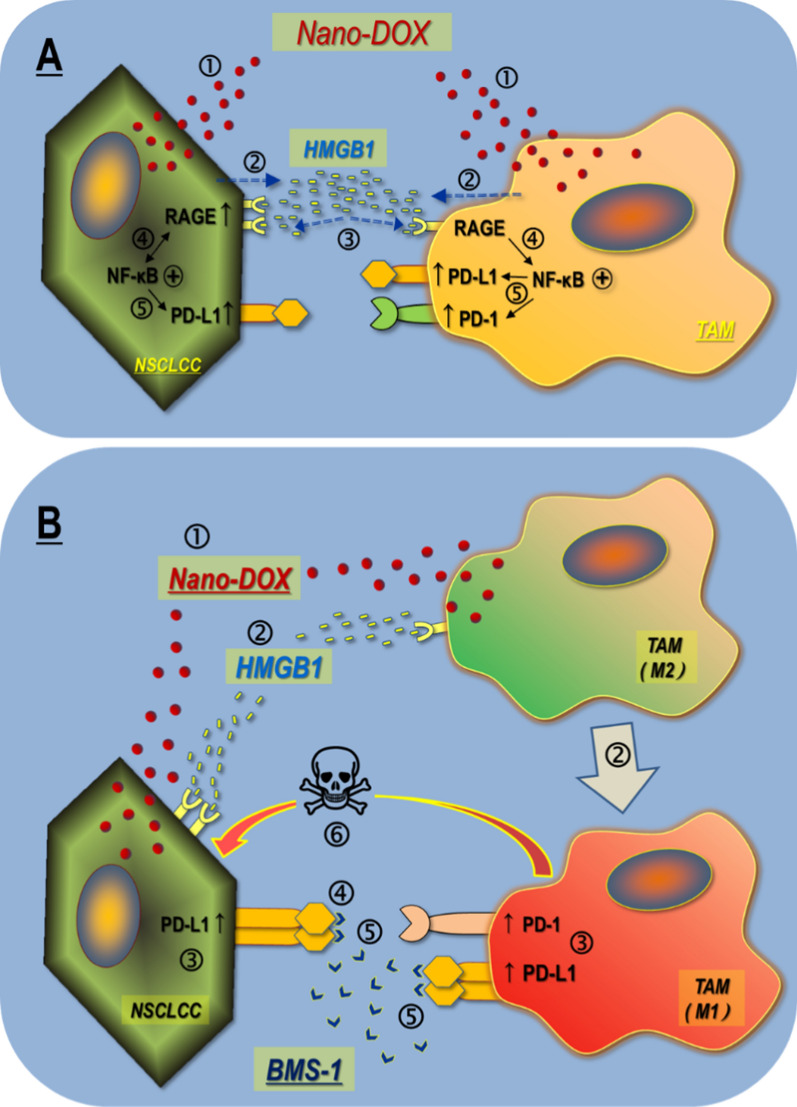
Fig. 11.
Main findings of this work. A Nano-DOX induce PD-L1 and PD-1 in the tumor cell-macrophage interaction through autocrine and paracrine activation of the HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB pathway. ➀ & ➁ Nano-DOX stimulates HMGB1 release from the NSCLCC & TAM. ➂ & ➃ HMGB1 binds with RGAE to activate NF-κB in the NSCLCC & TAMs. NF-κB activation also upregulates RAGE in the NSCLCC. ➄ Activated NF-κB upregulates PD-L1 in the NSCLCC. Activated NF-κB upregulates PD-L1 & PD-1 in the TAMs. B PD-L1 blocker BMS-1 enhances Nano-DOX-stimulated M1-like activation (anti-tumor phenotype) of TAMs via blocking PD-L1 induced by Nano-DOX in the lung cancer cells (NSCLC) and TAMs. ➀ Nano-DOX stimulates HMGB1 release from the NSCLCC & TAMs. ➁ HMGB1 bind with RAGE in the NSCLCC and TAMs. TAMs are repolarized to M1-like phenotype. ➂ PD-L1 are upregulated in the NSCLCC. Both PD-L1 and PD-1 are upregulated in the TAMs. ➃ BMS-1 blocks PD-L1 in the NSCLCC leading to growth suppression. ➄ BMS-1 prevents NSCLCC PD-L1 from binding with TAM PD-1 and blocks PD-L1 in the TAMs, thus enhancing M1-like TAM activation. ➅ M1-like TAMs suppress NSCLCC growth and induce apoptosis