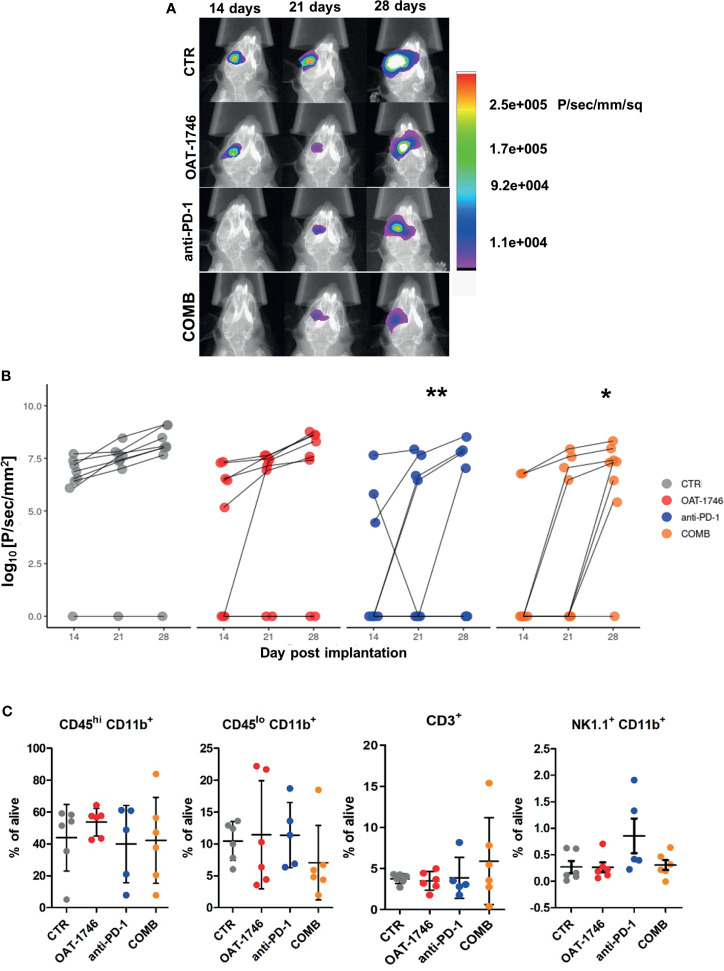
Figure 4.
Combined OAT-1746 and anti-PD-1 treatment reduces glioma growth. Mice were implanted with GL261 tdTomato+luc+ glioma cells and received saline (CTR), OAT-1746 (twice a day) alone or anti-PD-1 antibody at day 8, 10, 12 and 14 alone or in combination (COMB). (A) Representative images of tumor bioluminescence with Bruker Xtreme imaging. Color intensity represents a relative luciferase signal. Bioluminescence signals are plotted as photon/sec/mm2 against time at indicated days post-implantation. (B) Tumor size measured using in vivo bioluminescence imaging at various times post-implantation. The effect of treatment and time on tumor progression was assessed with factorial ANOVA; treatment effect F3,89= 4.801, p=0.004, day post-implantation effect F2,89 = 4.726, p=0.011, and Tukey HSD post hoc test: CTRL-OAT padj=0.455, CTRL-CHECK padj=0.005, CTRL-COMB padj=0.021, COMB-OAT-1746 padj=0.46, COMB-anti-PD-1 padj=0.96. (C) At day 28 post-implantation animals were perfused with PBS, control and tumor-bearing brains were removed and processed to isolate myeloid cells by FACS. Percentages of peripheral macrophages (CD11b+CD45hi), microglia (CD11b+CD45lo), CD3+ and NK1.1+ cells were evaluated. Significance of differences between groups was assessed with One-Way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. p-Values were considered as significant when **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05.