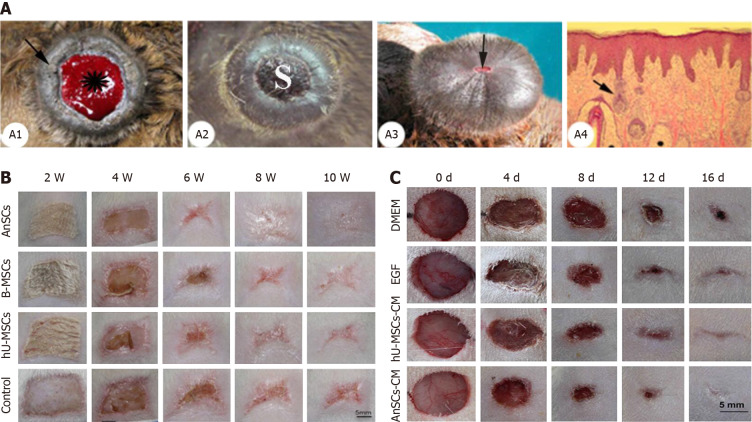
Figure 3.
Antler stem cells-induced wound healing process in deer and rats[38-40]. A: Wound healing over the top of a pedicle stump following casting of a bony antler. A1: Pedicle with a fresh casting surface. A2: Apical surface of a pedicle a few days after hard antler casting. A3: Apical view of a late wound healing-stage pedicle. The scab becomes negligible. A4: Histological section of sagittal-cut healing skin; B and C: Gross morphological changes during wound healing occurring either via direct injection of antler stem cells (AnSCs) into the rats (B) or topical application of conditioned medium of AnSCs on to the wounds (C). hU-MCSs: Human mesenchymal stem cells; B-MSCs: Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; AnSCs: Antler stem cells. Citation for Figure 3A[38]: Li C, Suttie JM. Histological studies of pedicle skin formation and its transformation to antler velvet in red deer (Cervus elaphus). Anat Rec 2000; 260: 62-71. Copyright © Li Chunyi. Published by Mapsci Digital Publisher OPC Pvt Ltd. Citation for Figure 3B[39]: Rong X, Zhang G, Yang Y, Gao C, Chu W, Sun H, Wang Y, Li C. Transplanted Antler Stem Cells Stimulated Regenerative Healing of Radiation-induced Cutaneous Wounds in Rats. Cell Transplant 2020; 29: 963689720951549. Copyright © The author(s). Published by SAGE Publications Inc. Citation for Figure 3C[40]: Rong X, Chu W, Zhang H, Wang Y, Qi X, Zhang G, Wang Y, Li C. Antler stem cell-conditioned medium stimulates regenerative wound healing in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther 2019; 10: 326. Copyright © The author(s). Published by BioMed Central.