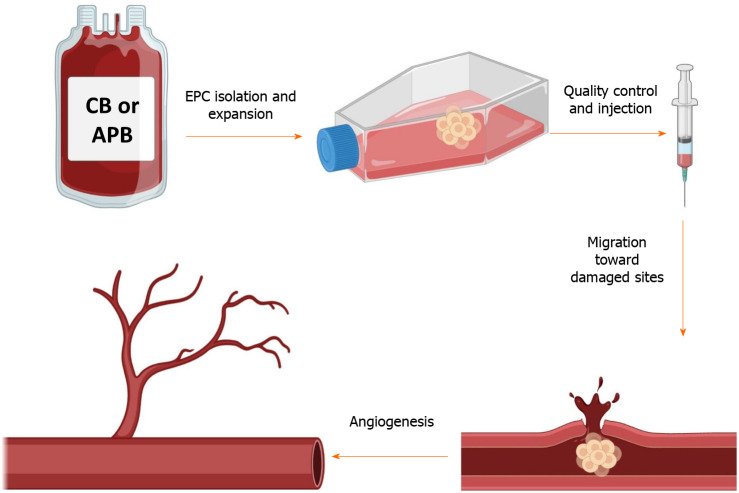
Figure 1.
This schematic depicts the simplified procedure from isolation to the application of endothelial progenitor cells. Briefly, endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are isolated from the cord blood or adult peripheral blood and are seeded on a culture flask. After the appearance of the first colonies (around 3 wk), cells are passaged and expanded to reach the desired numbers. After several verifications, EPCs could be injected into patients with cardiovascular disorders to take advantage of their regenerative and proangiogenic properties. The graphical images were created with BioRender.com. APB: Adult peripheral blood; CB: Cord blood.