Figure 7. Anp32e affects learning-induced transcription and memory formation.
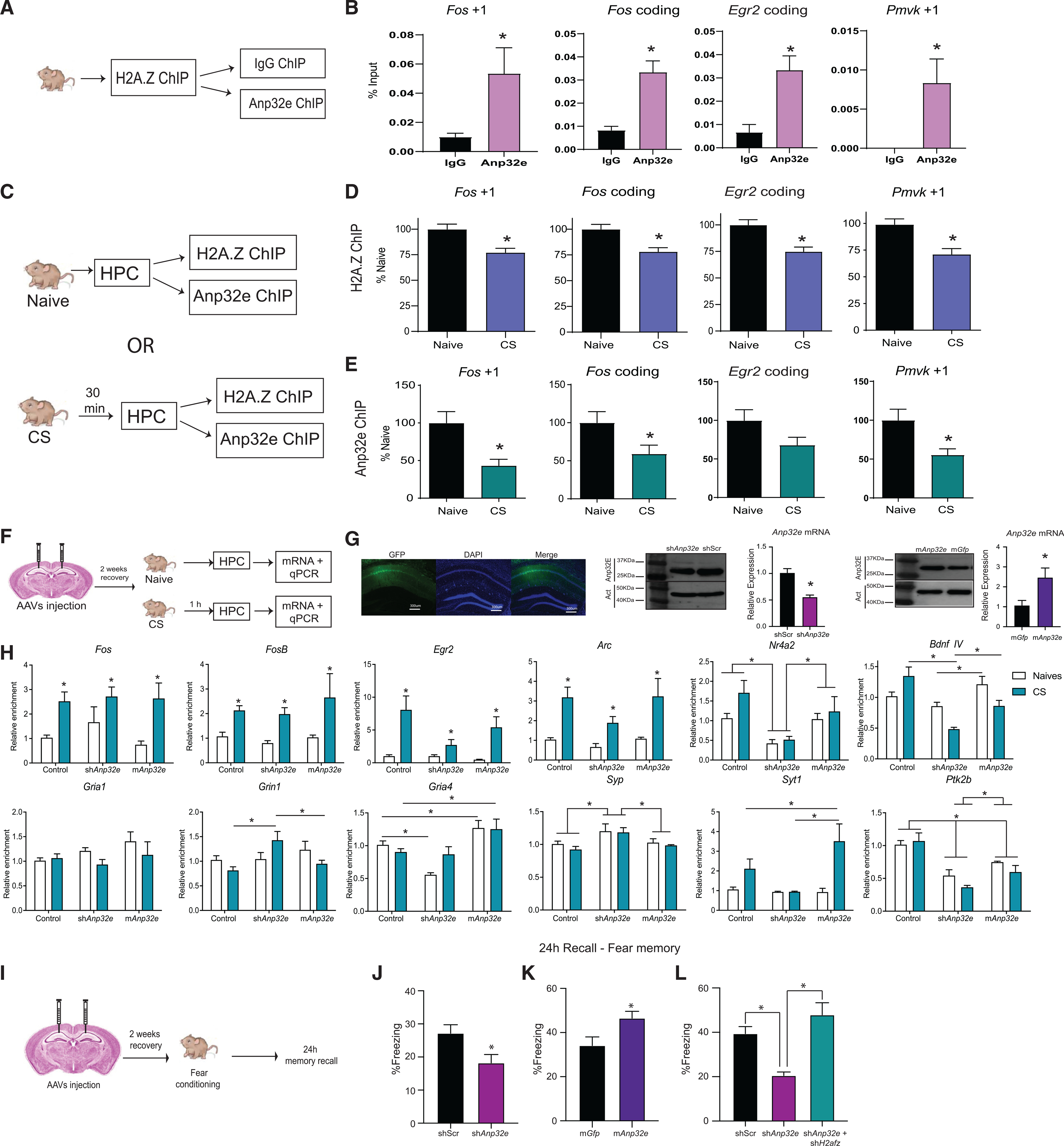
(A) Schematic representation of the ChIP-re-ChIP workflow. Mouse hippocampus was extracted and processed first for H2A.Z ChIP, followed by a second ChIP against Anp32e, using IgG as a control for non-specific binding.
(B) ChIP-re-ChIP showing Anp32e (pink) enrichment on H2A.Z-bound genomic sites (n = 5 or 6/group).
(C) Schematic representation of the experimental workflow.
(D and E) Separate ChIP analyses for (D) H2A.Z and (E) Anp32E were conducted for samples from the same mice under baseline conditions and 30 min after contextual fear conditioning. Both proteins had reduced binding at the first nucleosome downstream (+1 nucleosome) of the TSS and in the coding region of several H2A.Z-associated genes 30 min after fear conditioning (n = 15–25/group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. p values are from two-tailed unpaired t tests. *p ≤ 0.05.
(F) Schematic representation of the experimental workflow. Mice received stereotaxic injections of AAV vectors to either deplete or overexpress Anp32e and effects on learning-induced gene expression were assessed 1 h after contextual fear conditioning.
(G) Representative image of virus spread in the hippocampus (left) and mRNA levels and western blots showing Anp32e depletion and overexpression in areaCA1.
(H) AAV-mediated gene depletion or overexpression of Anp32e alters baseline and learning-induced gene expression of neuronal genes 1 h after fear conditioning(n = 3–6/group). *p ≤ 0.05.
(I) Schematic representation of the surgeries and behavioral testing timeline.
(J) Anp32e depletion impairs fear memory (n = 16/group).
(K) Anp32e overexpression enhances fear memory (n = 16/group).
(L) Simultaneous knockdown of Anp32e and H2afz (green bar) restores fear memory (n = 8 or 9/group). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05.
