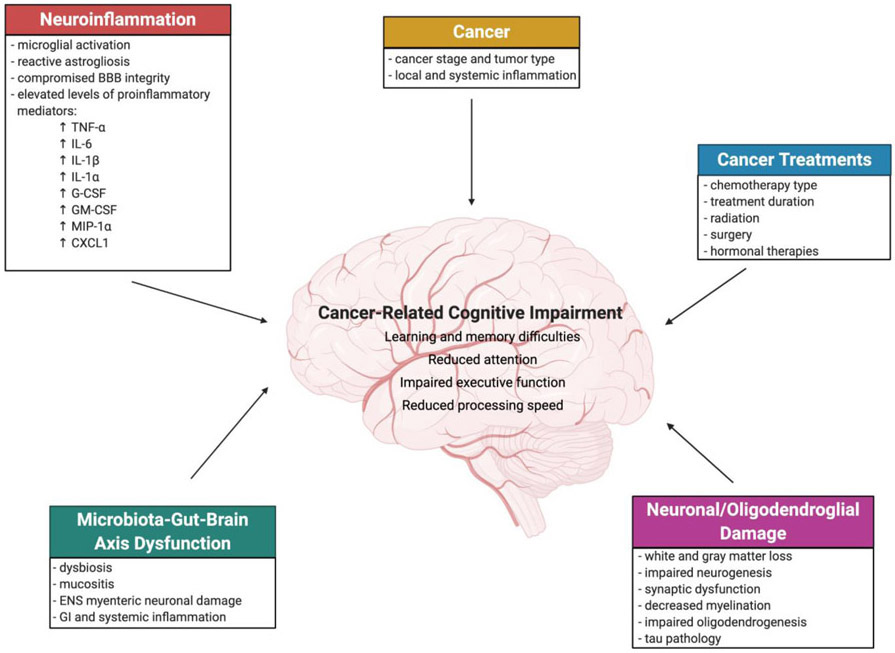
Figure 1. Mechanisms of cancer-related cognitive impairment (CRCI).
A simplified schematic providing an overview of mechanisms of CRCI discussed in this review. Cancer-induced cognitive changes may be associated with local and systemic inflammation, and elevated production of proinflammatory mediators, which can induce neuroinflammation. Cancer treatments, in particular chemotherapy which is discussed here, is associated with neuronal/oligodendroglial damage, neuroinflammation, and microbiota-gut-brain axis dysfunction, which can directly or indirectly induce cognitive decline. Cancer and cancer treatments may exert additive detrimental effects on cognition.