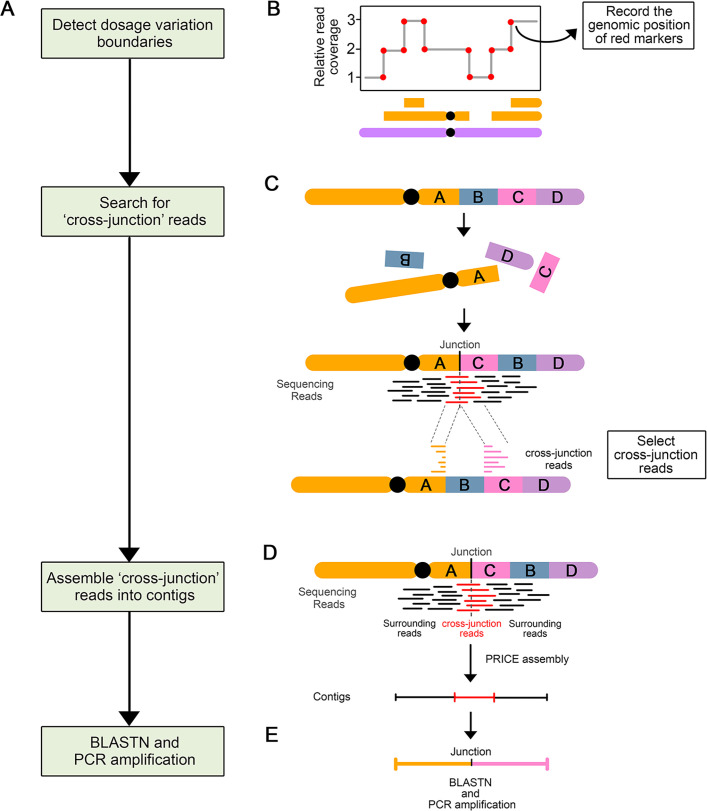
Fig 3. Process of novel DNA junctions selection and validation.
(A) Flow chart illustrating the steps involved in novel DNA junction detection, selection, and validation. (B-E) Diagram illustrating the approach involved in each step. (B) A schematic dosage plot showing a genomic region containing many instances of dosage variations. The red dots highlight the boundaries of every indel and constituting potential breakpoint positions. (C) Schematic diagram illustrating the origin and mapping behavior of cross-junction reads. After chromosomal rearrangement, fragment A and C joined together and formed a novel DNA junction. The sequencing reads (in red) that crossed this novel DNA junction are called cross-junction reads. These cross-junction reads map onto two different locations on the reference genome. (D) Assembly of the novel DNA junctions. Cross-junction reads are assembled into one contig using the PRICE assembler. (E) Each newly assembled scaffold is compared to the reference genome using BLASTN to: (i) find out the exact alignment positions of two breakpoints of the novel junction; (ii) confirm the uniqueness of contigs.