Figure 3.
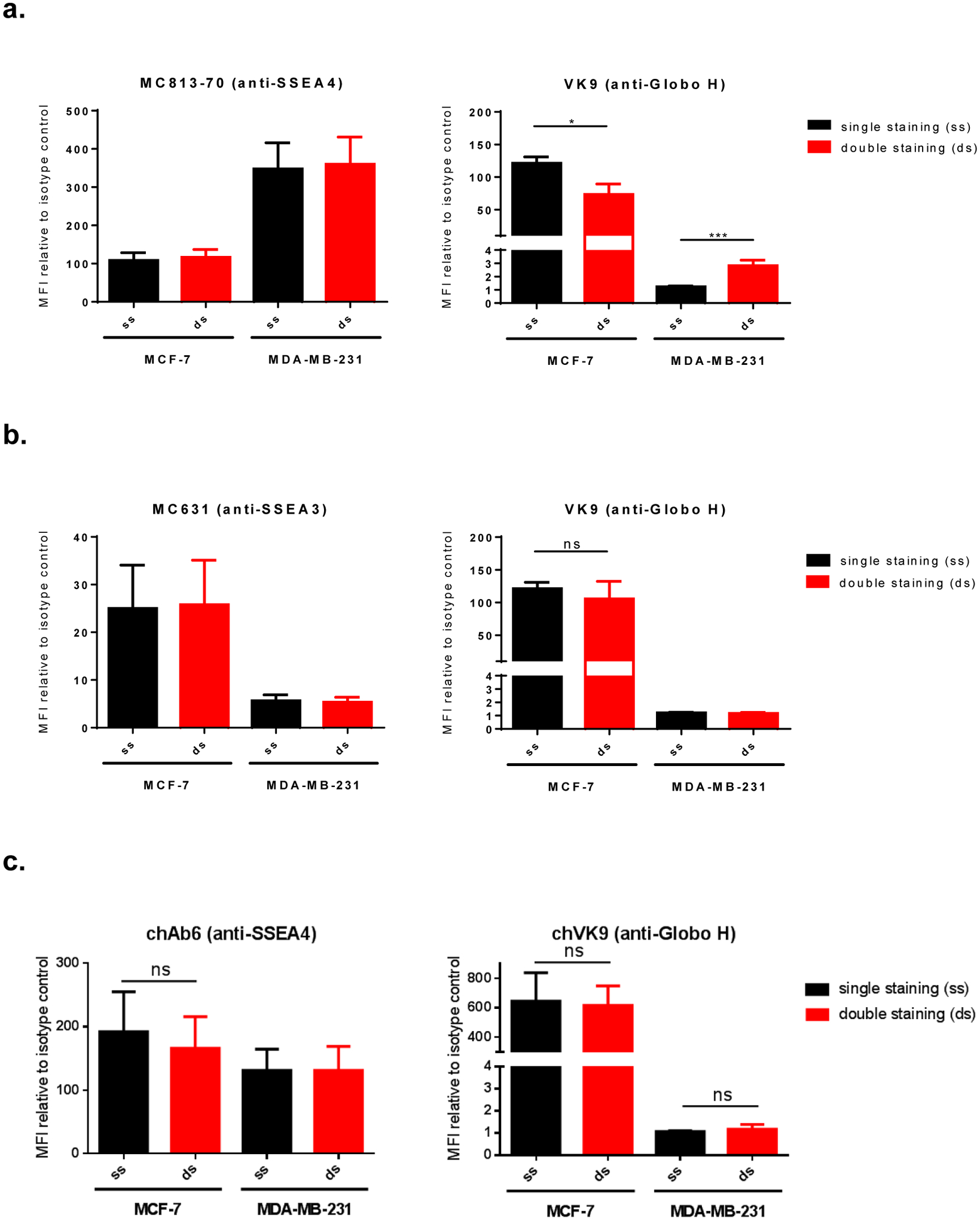
Surface staining of globo-series GSLs on MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. a, Double staining of SSEA4 and Globo H using AF488-conjugated MC813–70 and APC-conjugated VK9 (mouse antibodies). VK9 signal difference was observed: MCF-7 showed reduced double staining signal, while MDA-MB-231 showed increased double staining signal. This indicates that VK9 does not affect antigen binding of MC813–70, but MC813–70 affects antigen binding of VK9. The scatter plots are provided in Figure S1. b, Double staining of SSEA3 and Globo H using AF488-conjugated MC631 and APC-conjugated VK9 (mouse antibodies). Single staining and double staining signals were similar for both MC631 and VK9, indicating the two antibodies do not affect each other when binding antigens. c, Double staining of SSEA4 and Globo H using FITC-conjugated chAb6 and APC-conjugated chVK9 antibodies. Single staining and double staining signals were similar for both chAb6 and chVK9, indicating the two antibodies do not affect each other when binding antigens. To determine whether the two antibodies influence each other when binding antigens, we compared the staining signals mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs, represent the geometric mean intensities) relative to isotype control between single staining (ss, in black) and double staining (ds, in red) in each cell line.
