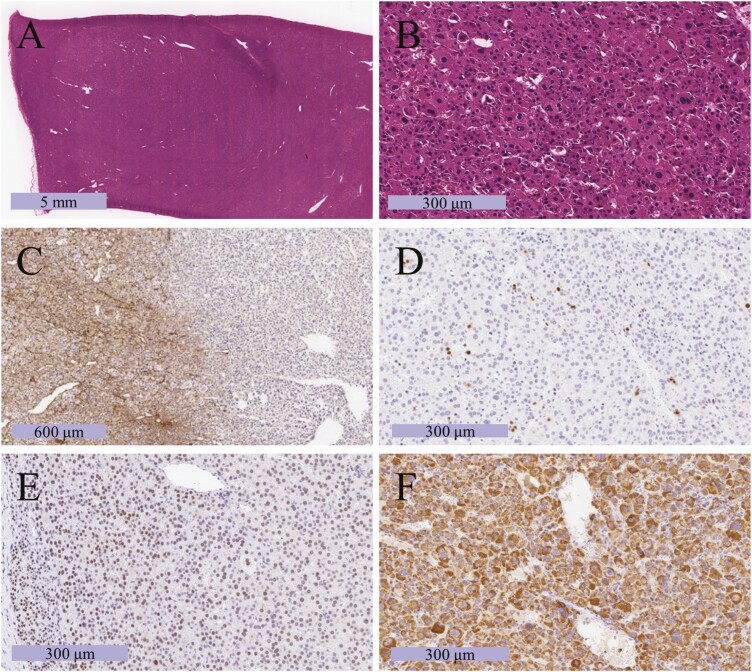
Figure 2.
Photomicrograph of the resected tumor. (A, B) Hematoxylin and eosin staining in low-power (A) and high-power (B) fields. (C) Immunohistochemical labeling for type IV collagen, which can confirm the presence of diffuse proliferation by checking whether the basic chordal structure has been destroyed or not. (D) Immunohistochemical labeling for Ki-67, which can stain cell nuclei during all active phases of the cell cycle and is used as a marker of cell proliferation. The Ki-67 labeling index was 6%. (E) Immunohistochemical labeling for SF-1, which can stain cell nuclei derived from steroidogenic hormone-producing glands such as the adrenal cortex [10]. (F) Immunohistochemical labeling for mitochondria. In the case of the oncocytic tumor, mitochondrial staining can be observed throughout the cytoplasm.