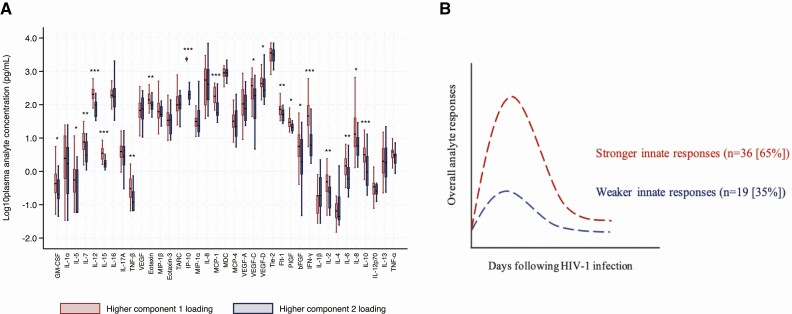
Figure 5.
(A) Graph demonstrating the differentiation of analyte responses by principal component analysis loadings. Volunteers with higher principal component (PC) 1 loadings had significantly higher plasma concentration in a majority of the analytes compared to those with higher PC2 loadings (Wilcoxon rank sum test P < .05 [*], P < .01 [**], and P < .001 [***], N = 55); (B) A schematic illustration of the differentiation of analyte responses into volunteers with and without a cytokine storm; and Wilcoxon signed rank test (P < .05 [*], P < .01 [**], P < .005 [***], and P < .0005 [****]; paired/matched signed rank test in green, N = 31). Abbreviations: hbFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; Flt, FMS-like tyrosine kinase; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; hAHI, hyperacute HIV-1 infection; HIV-1, human immunodeficiency virus type 1; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; IP, interferon gamma-induced protein; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; MDC, macrophage-derived chemokine; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; PlGF, placental growth factor; TARC, thymus and activation-related chemokine; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.