Fig. 5.
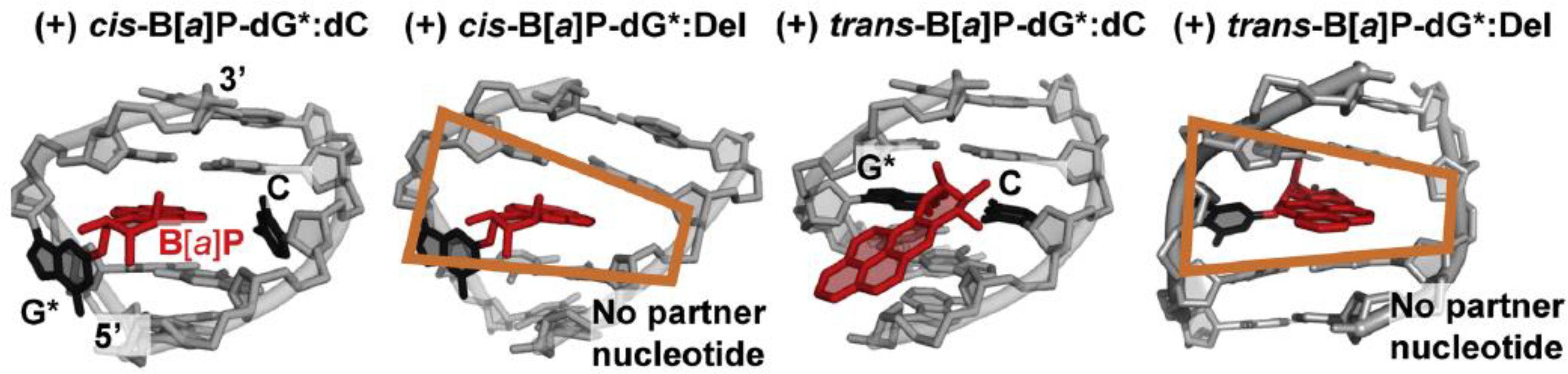
NMR solution structures of the (+)-cis-B[a]P-G*:C, (+) cis-B[a]P-G*:Del, (+)trans-B[a]P-G*:C and (+) trans-B[a]P-G*:Del duplexes. The (+) cis-B[a]P-G*:C is base-displaced intercalated with B[a]P rings intercalated into the duplex, the deoxyguanosine G* is displaced into the minor groove, and the partner C is displaced into the major groove. In the case of the (+) cis-B[a]P-G*:Del, the G* is displaced into the minor groove, and the absence of the partner C nucleotide gives rise to a wedge shaped intercalation pocket (orange frame) that enhances B[a]P aromatic ring stacking with adjacent base pairs. The full duplex (+) trans-B[a]P-G*:C has the aromatic ring system in the minor groove directed toward the 5′end of the modified strand. The (+)-trans-G*:Del structure resembles the intercalated (+)-cis-G*:Del structure, except that the modified deoxyguanosine is displaced into the major groove (trans) whereas it is displaced into the minor groove in the case of the (+)-cis G*:Del lesion.
