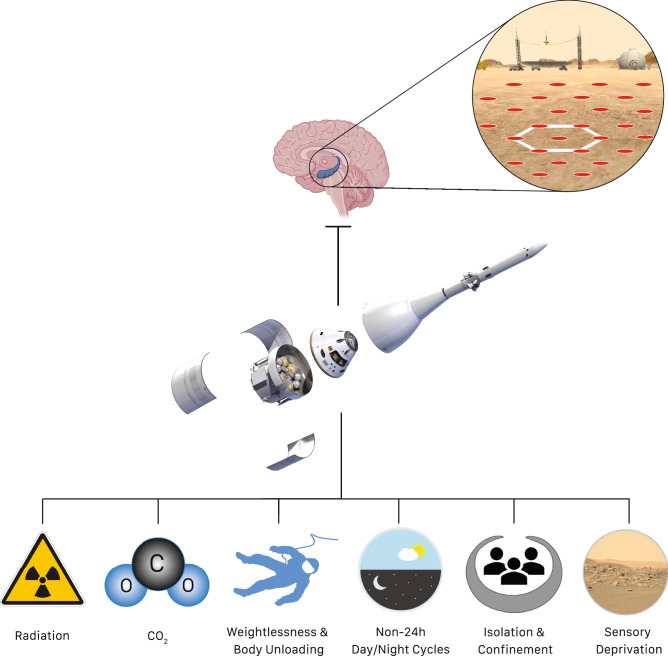
Fig. 2.
Environmental, operational, and psychological stressors associated with spaceflight. Ionizing radiation, hypercapnia (increased CO2 levels), altered vestibular stimulation and reduced physical activity in response to weightlessness, circadian disruptions and poor sleep due to altered day and night cycles, isolation and confinement, and sensory deprivation can have adverse effects on hippocampal plasticity. The hippocampus is critical for declarative memory formation, emotion processing, and spatial cognition. Together with the entorhinal cortex, the hippocampus supports the encoding, consolidation, and retrieval of spatial information by processing information about location (place cells of the hippocampus) relative to a grid map characterized by a hexagonal pattern (grid cells in the entorhinal cortex). Picture Credit: Schematic brain and hippocampus were created with BioRender.com. Spacecraft (middle) and right icon in bottom row (sensory deprivation): NASA; astronaut silhouette (third icon, bottom row) by Natasha Sinegina/CC BY); icon depicting Non-24h Day/Night cycles by icon-library.com