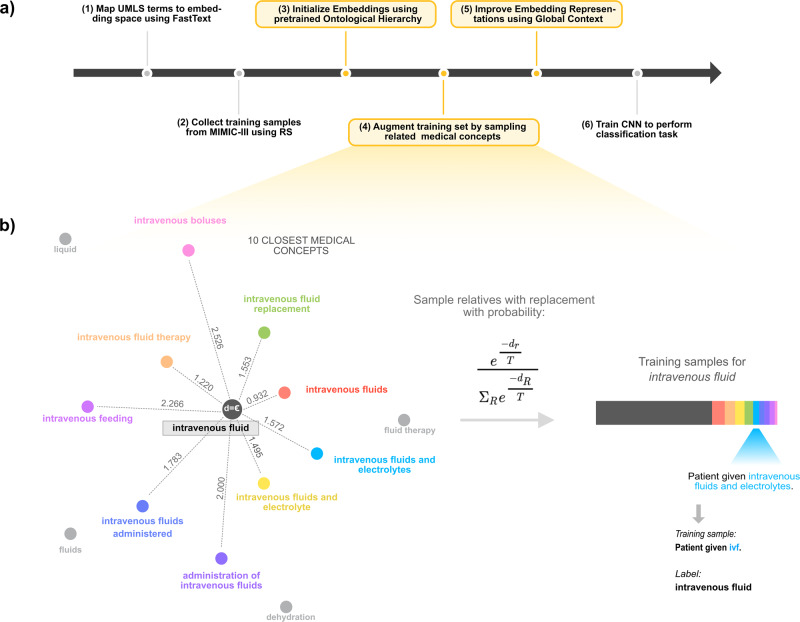
Fig. 1. Overview of our abbreviation disambiguation pipeline for data collection and model training.
a Overview of our method. Our key contributions are indicated with yellow boxes. b Illustration of data augmentation technique for the training set. For each expansion, we sample sentences for the ten closest medical concepts using reverse substitution (RS) with a probability proportional to their Euclidean distance in the embedding space. The Euclidean distance is shown above the dotted line connecting the expansion to its relative. The probability of sampling is indicated above the arrow. dr is the Euclidean distance between the expansion and relative and R refers to the ten closest medical concepts. During training, we learn a temperature T using Bayesian optimization that is used in the sampling function. In the event that an expansion is present in the training corpus, we sample it with a distance of ε, which we set to 0.001. We add each sample to our training set by replacing the relative with the abbreviation and using the target expansion as the label. An example of this is shown below the color bar. The color of each relative corresponds to the color in the bar to the right of the arrow, which reflects the proportion of the training set composed by that relative.