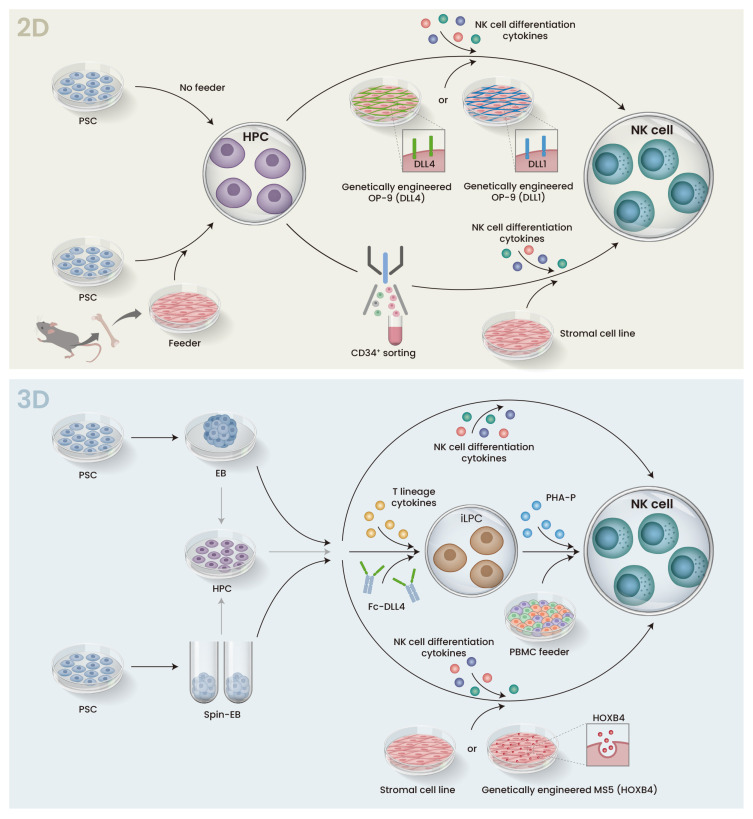
Fig. 3. Schematic representation of 2D and 3D protocols for iPSC differentiation to NK cells.
Both 2D and 3D protocols are broken into two stages. The first stage differentiates PSCs into HPCs, and the HPCs are then cultured with a cytokine cocktail that induces NK cell differentiation in the second stage. (Top) In the 2D protocol, PSCs are co-cultured with murine bone marrow stromal cells (feeder) to promote hematopoietic differentiation. In the subsequent step, CD34+ HPCs are sorted and transferred to a second stromal cell line. Alternatively, sorting can be avoided, and the cells are transferred onto a stromal cell line such as OP-9 that is engineered to express DLL4 or DLL1. In either case, cytokines such as IL-15 are added to promote NK cell differentiation. (Bottom) In the 3D protocol, HPC differentiation is performed in suspension culture via EB or Spin-EB formation. The EBs are directly transferred to feeder stromal cell lines or feeder-free conditions, or HPCs are dissociated from the EBs and transferred. In either case, cytokines are added to induce NK cell differentiation. iLPC, iPSC-derived lymphocyte progenitor cells; PHA-P, phytohemagglutinin-P; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.