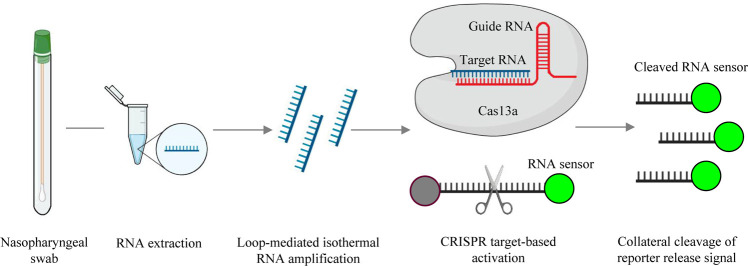
Fig. 3.
A schematic illustration of the SHERLOCK detection assay.
Using nasopharyngeal swabs as an example, conventional RNA extraction is used as the input and is followed by reverse transcription and loop-mediated isothermal amplification. The CRISPR-Cas13-RNA complex is activated by binding to a complementary RNA target, while CRISPR-Cas13 exhibits nonspecific endonuclease activity, which activates and cleaves fluorescent RNA sensors. The fluorescent RNA sensor is quenched when it is intact, whereas it emits fluorescent signals when it is cleaved by the activated CRISPR-Cas13 complex.