Figure 1.
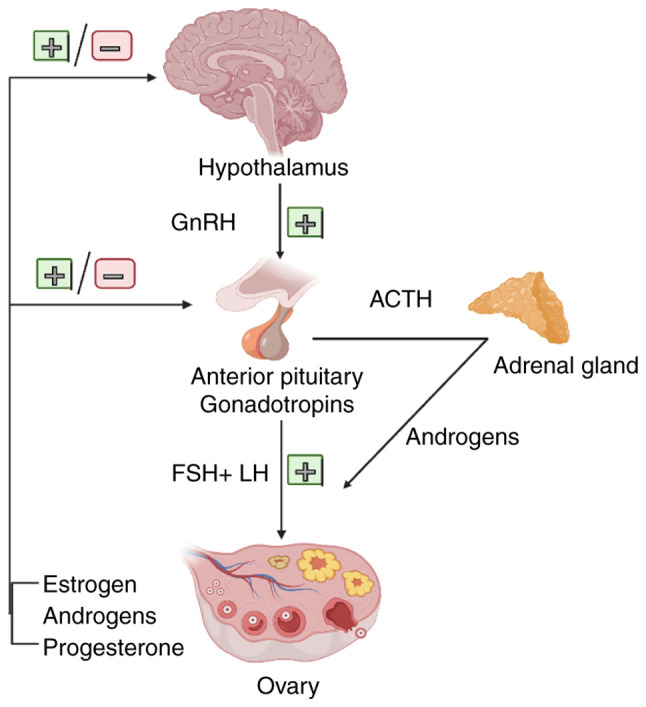
Hormonal environment of the ovaries. The endocrine regulation of ovary is primarily directed by the neuroendocrine actions of the HPO axis. Proper development and organization of the HPO axis are indispensable for normal female fertility. The basic molecule regulating the function of the HPO axis is GnRH. The episodic and timely secretion of GnRH from the hypothalamus and the activation of the pituitary GnRH-R are essential for the synthesis and secretion of gonadotropins (FSH and LH). The ovarian tissue secretes mainly estrogen, progesterone and androgens, which together with a small amount of androgens from the adrenal cortex regulate the development of ovarian tissue and the maturation of follicles for release (the figure was created using biorender.com). HPO, hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; GnRH-R, GnRH receptor; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotrophic hormone.
