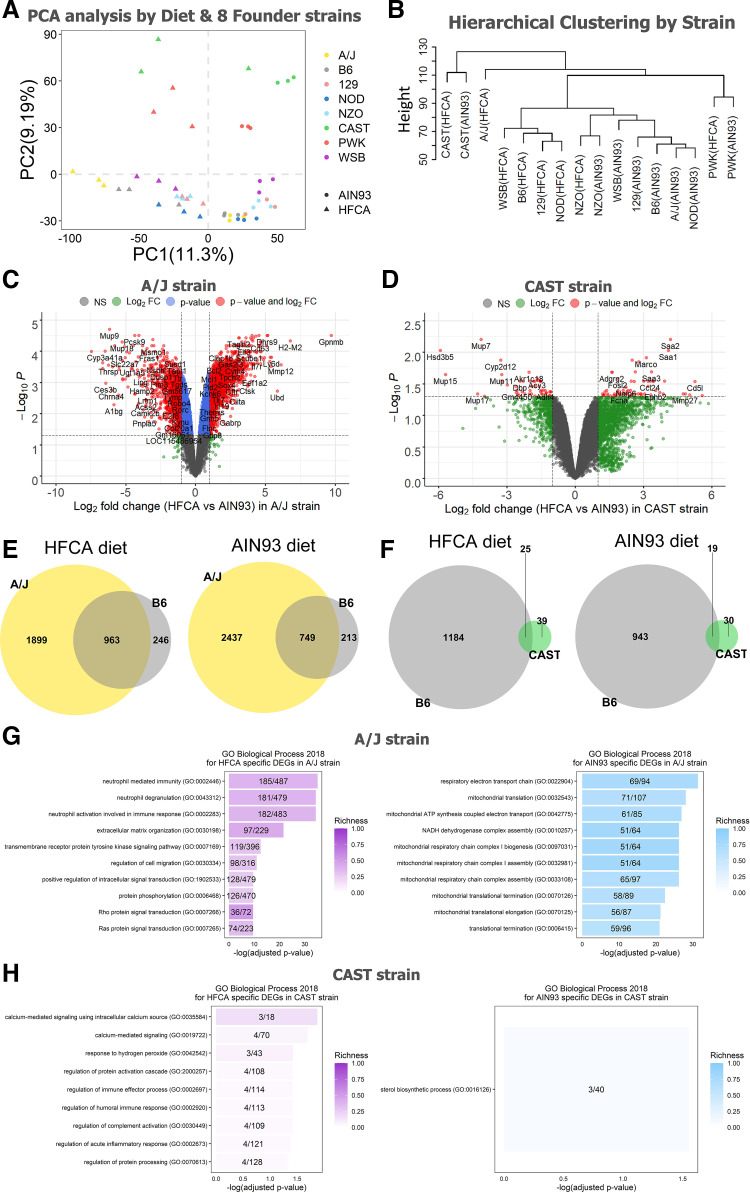
Figure 2.
Effect of genetic background on hepatic gene expression in the eight Collaborative Cross (CC) founder strains in female mice. Principal component analysis from AIN-93M diet or HFCA diet (A) and hierarchical clustering (B) determined that the major source of variation in gene expression was due to genetic variation among the eight strains. Venn diagrams to identify overlapping upregulated genes between A/J strain and B6 strain (C) and between CAST strain and B6 strain (D) in each diet. Volcano plots between high-fat and cholic acid (HFCA) diet and AIN-93M diet in liver gene expression in A/J strain (E) and CAST strain (F). Horizontal dotted lines indicate adj. P < 0.05, vertical dotted gray lines indicate a twofold difference. Top 10 GO terms of upregulated genes in HFCA diet and AIN-93M diet identified in enrichment analysis in A/J strain (G) and CAST strain (H). Pathways were ordered from top to bottom by significance (highest to lowest) and colored by gene richness. n = 6 mice for each founder, three for AIN-93M diet and three for HFCA diet-fed mice. A/J (yellow), B6 (gray), C57BL/6J; 129 (pink), 129S1/SvlmJ; NOD (blue), NOD/ShiLtJ; NZO (light blue), NZO/HILtJ; CAST (green), CAST/EiJ; PWJ (red), PWK/PhJ; WSB (purple), WSB/EiJ.