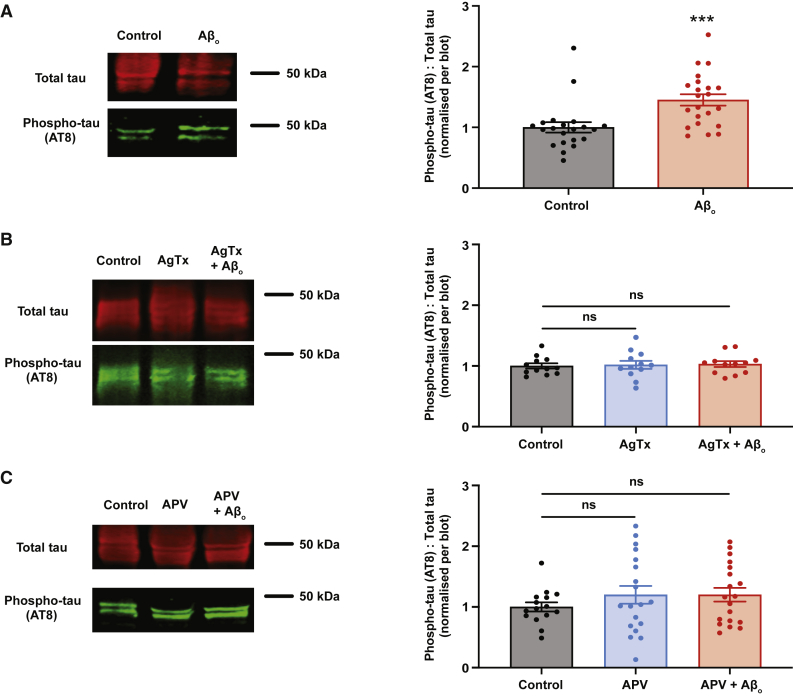
Figure 2.
Aβo-mediated hyperphosphorylation of tau requires enhancement of glutamate release probability
(A) Western blot analysis of hippocampal slices treated for 7 days as indicated. Left panels show representative bands. The ratio of pathologically phosphorylated tau (AT8 antibody) to total tau was quantified and normalized to control within each blot (control: n = 21, 1.00 ± 0.09; Aβo: n = 22, 1.45 ± 0.09).
(B) Western blot analysis of hippocampal slices treated for 7 days as indicated. Low-dose (50 nM) ω-agatoxin IVA (AgTx) treatment restores elevated release probability to normal levels (Jeans et al., 2020). Left panels show representative bands. The ratio of pathologically phosphorylated tau (AT8 antibody) to total tau was quantified and normalized to control within each blot (control: n = 12, 1.00 ± 0.04; AgTx: n = 12, 1.02 ± 0.07; AgTx + Aβo: n = 12, 1.03 ± 0.05). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test versus control.
(C) Western blot analysis of hippocampal slices treated for 7 days as indicated. Left panels show representative bands. The ratio of pathologically phosphorylated tau (AT8 antibody) to total tau was quantified and normalized to control within each blot (control: n = 15, 1.00 ± 0.08; APV: n = 19, 1.20 ± 0.15; APV + Aβo: n = 19, 1.20 ± 0.11).
One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test versus control. Error bars represent ± SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. ns, not significant.