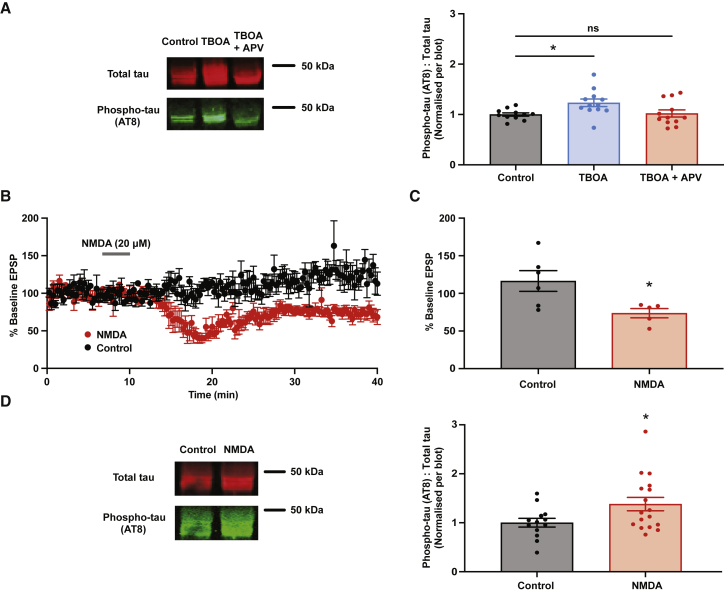
Figure 3.
Chronic induction of chemical LTD drives pathological hyperphosphorylation of tau
(A) Incubation with the inhibitor of glutamate uptake TBOA increases tau phosphorylation in an NMDAR-dependent manner. Western blot analysis of hippocampal slices treated for 7 days as indicated. Left panel shows representative bands. The ratio of pathologically phosphorylated tau (AT8 antibody) to total tau was quantified and normalized to control within each blot (control: n = 11, 1.00 ± 0.03; TBOA: n = 12, 1.23 ± 0.08; TBOA + APV: n = 12, 1.02 ± 0.07). One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test versus control.
(B) Summary traces of patch-clamp recordings showing slope of EPSP at CA3-CA1 synapses following addition of NMDA compared with control. Traces normalized to pre-addition baseline.
(C) Mean average EPSP slopes calculated within a 25- to 30-min time window after NMDA application (control: n = 6, 116.4% ± 13.75%; NMDA: n = 5, 73.63% ± 6.12%).
(D) Western blot analysis of hippocampal slices treated for 7 days as indicated. Left panel shows representative bands. The ratio of pathologically phosphorylated tau (AT8 antibody) to total tau was quantified and normalized to control within each blot (control: n = 13, 1.00 ± 0.09; NMDA: n = 17, 1.38 ± 0.14).
Error bars represent ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05.