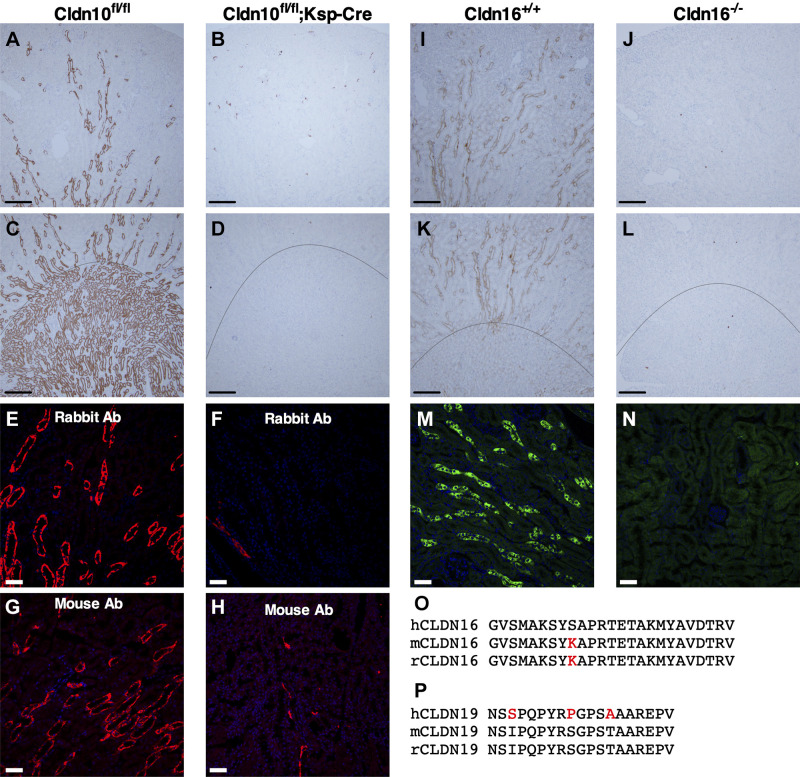
Figure 1.
Validation of anticlaudin (CLDN)16 and anti-CLDN10 antibodies (Ab) in wild-type (WT) mice and Cldn16- or Cldn10-specific knockout (KO) mice. A–D: immunohistochemistry for CLDN10 in paraffin-embedded cortical and medullary kidney tissue from WT (Cldn10fl/fl; A and C) and Cldn10 KO mice with kidney-specific deletion (Cldn10fl/fl;Ksp-Cre; B and D). A and B: cortex/outer stripe of the outer medulla (OSOM), C and D: outer medulla. Scale bars = 200 µm. E−H: immunofluorescence for CLDN10 in the outer medulla from WT (E: rabbit anti-CLDN10 antibody and G: mouse anti-CLDN10 antibody) and Cldn10 knockout mice with kidney-specific deletion (F: rabbit anti-CLDN10 antibody and H: mouse anti-CLDN10 antibody). Scale bars = 50 µm. I−L: immunohistochemistry for CLDN16 in paraffin-embedded cortical and medullary kidney tissue from WT (Cldn16+/+) mice [I: cortex/OSOM and K: OSOM/inner stripe of the outer medulla (ISOM)] and Cldn16 KO (Cldn16−/−) mice (J: cortex/OSOM and L: OSOM/ISOM). Scale bars = 200 µm. M and N: immunofluorescence for CLDN16 in frozen cortical kidney tissue from WT (M) and Cldn16 KO mice (N). Scale bars = 50 µm. The line indicates the border between the ISOM and OSOM. O and P: alignments of the parts of the amino acid sequence of CLDN16 (O) and CLDN19 (P) from the human, mouse, and rat used to generate antibodies: anti-CLDN16 antibody was generated against the human epitope and anti-CLDN19 antibody was generated against the mouse epitope. The differences between human and rodent sequences are shown in red.