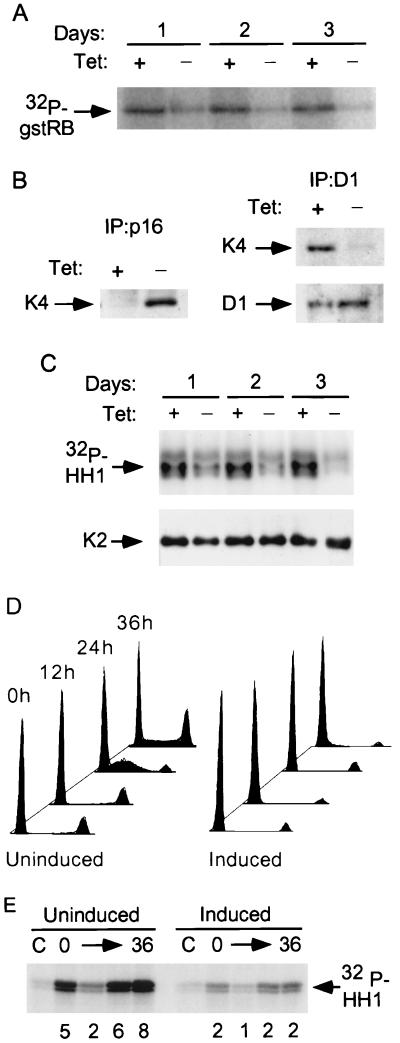
FIG. 1.
p16 mediates inhibition of both cdk4 and cdk2 in OSp16.1 cells. (A) Inhibition of cdk4 kinase activity. Extracts were prepared from cells cultured with (+) or without (−) TET (1 μg/ml) for 1 to 3 days and were normalized for protein content. cdk4 was immunoprecipitated, and its kinase activity was assayed using gstRB as a substrate. (B) (Left panel) Binding of p16 to cdk4. Extracts were prepared from cells cultured with or without TET for 3 days and were normalized for protein content. p16 complexes were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted for cdk4 (K4). (Right panel) Inhibition of cyclin D1 binding to cdk4 on p16 induction. Extracts were prepared from cells that were or were not subjected to p16 induction for 3 days. Cyclin D1 complexes were immunoprecipitated (D1). These samples were normalized for cyclin D1 content by immunoblotting (below) and immunoblotted for cdk4 (K4). (C) Inhibition of cyclin E-associated kinase activity. Extracts were prepared from cells that were or were not subjected to p16 induction for 1 to 3 days. Cyclin E complexes were immunoprecipitated and normalized for cdk2 content by immunoblotting (K2) (shown below). Kinase activities were then assayed using histone H1 (HH1) as a substrate. (D) p16 induction prevents S phase entry following cell cycle synchronization with lovastatin and rescue with mevalonic acid. OSp16.1 cells were treated with lovastatin for 40 h in the presence (Uninduced) and absence (Induced) of TET. At the end of this period, a portion of the cells was harvested and assayed for DNA content by flow cytometry (0 h; x axis, DNA content; y axis, cell number, normalized to each G1 peak). The lovastatin block was rescued in the remaining cells by addition of mevalonic acid for another 36 h. Cells were removed at 12-h intervals for analysis. The S phase fraction at 24 h was 43% in the uninduced cells versus 5% in the induced cells. (E) Inhibition of cyclin E-associated kinase activity by p16 induction in synchronized cells. Extracts were prepared from cells treated as described for panel D and normalized for protein content. Cyclin E complexes were immunoprecipitated, and their kinase activities were assayed using histone H1 (HH1) as a substrate. C, control (employing nonspecific rabbit IgG). The relative signal intensity is given below each lane.