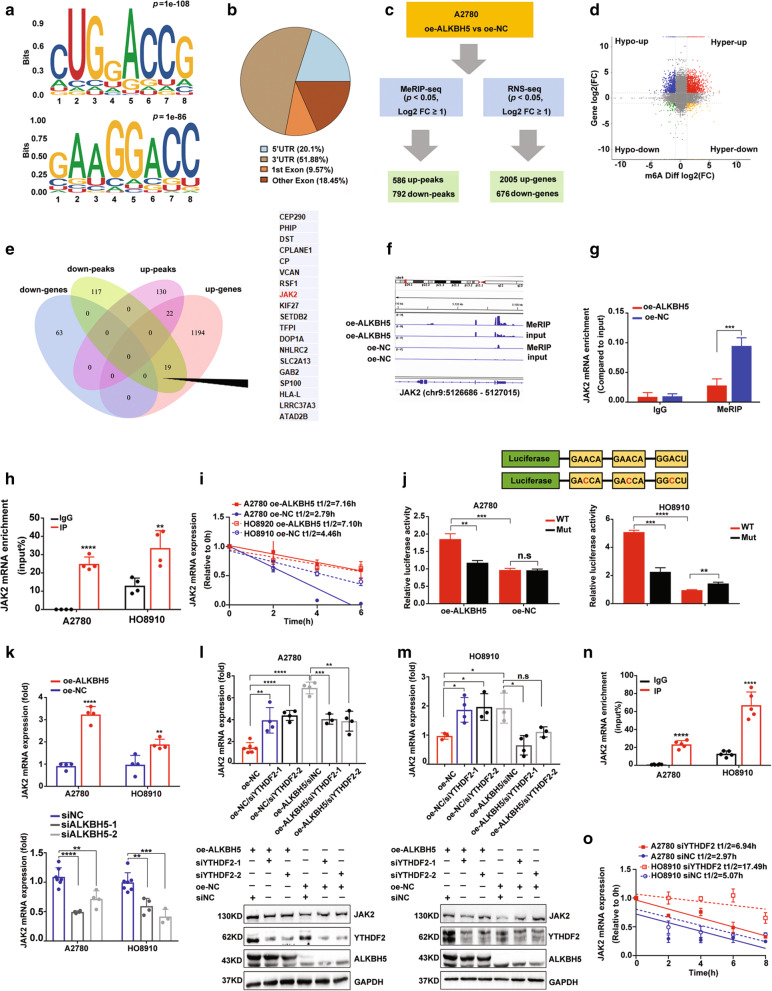
Fig. 4.
ALKBH5 erases m6A modifications of JAK2 mRNA and maintains JAK2 mRNA expression by lowering YTHDF2-mediated mRNA degradation. (a) The two differentially enriched m6A-modification motif in the immunopurified RNA in A2780. (b) Distribution of regulated m6A peaks in mRNA is detected by MeRIP-seq after ALKBH5 overexpression. (c) Schematic of downstream analysis for MeRIP-Seq and RNA-seq. (d) The quadrantal diagram graph displays the transcripts with different m6A peaks and regulated gene expression based on MeRIP-seq and RNA-seq. (e) The Venn diagram shows the genes detected by MeRIP-seq and RNA-seq; the 19 candidate target genes of ALKBH5 are shown on the right. (f) m6A abundances in JAK2 mRNA transcripts in cells with ALKBH5 overexpression (MeRIP and input) and in negative control (MeRIP and input). m6A regulation is calculated as the ratio of m6A abundances of MeRIP to input (log2FC = − 2, p = 0.03). (g) MeRIP-qPCR confirms that ALKBH5 down-regulates the m6A peak in 3’UTR of JAK2 mRNA. (h) RIP-qPCR confirmed JAK2 mRNA binding to ALKBH5. (i) The Act-D assay shows an increased lifespan of JAK2 mRNA after ALKBH5 overexpression. (j) Relative luciferase activity of the wild-type or mutant JAK2 3′UTR luciferase reporter in EOC cells with ALKBH5 overexpression and the negative control. (k) ALKBH5 positively regulates JAK2 mRNA expression in EOC cells. (l and m) YTHDF2 remarkably regulates JAK2 expression in A2780 and HO8910. (n) RIP-qPCR confirms YTHDF2 binding to JAK2 mRNA. (o) Increased lifespan of JAK2 mRNA after YTHDF2 silencing