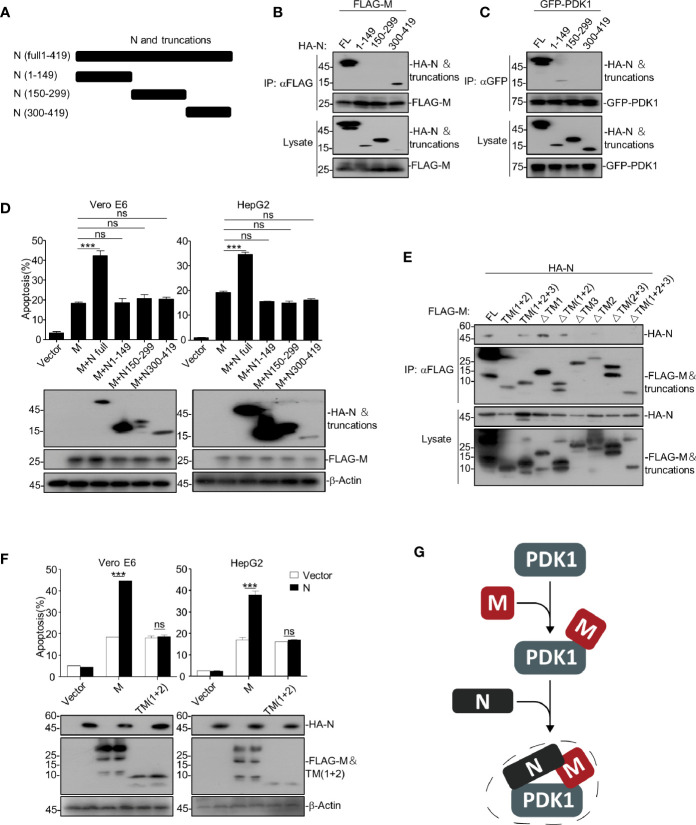
Figure 4.
SARS-CoV-2 N enhances M-induced apoptosis via interacting with both M and PDK1. (A) Schematic representation of SARS-CoV-2 N and its truncations. (B, C) HEK293T cells transfected with HA-SARS-CoV-2 N and its truncations together with FLAG-SARS-CoV-2 M and GFP-PDK1, respectively. After 24 h, cells were collected for co-immunoprecipitation (with anti-FLAG or anti-GFP) and Western blotting (with anti-GFP, anti-HA, or anti-FLAG). (D) Vero E6 and HepG2 cells were transfected with FLAG-SARS-CoV-2 M together with HA-SARS-CoV-2 N and its truncations, respectively. After 24 h, cells were collected for Western blotting (with anti-FLAG, anti-HA, or anti-β-Actin) or stained with Annexin V-FITC/PI for flow cytometry analysis, and the percentage of apoptotic cells were measured. (E) HEK293T cells transfected with FLAG-SARS-CoV-2 M and its truncations together with HA-N. After 24 h, cells were collected for coimmunoprecipitation (with anti-FLAG) and Western blotting (with anti-FLAG or anti-HA). (F) Vero E6 and HepG2 cells were transfected with FLAG-SARS-CoV-2 M and FLAG-SARS-CoV-2 M TM(1 + 2) together with HA-SARS-CoV-2 N. After 24 h, cells were collected for Western blotting (with anti-FLAG, anti-HA, or anti-β-Actin) or stained with Annexin V-FITC/PI for flow cytometry analysis, and the percentage of apoptotic cells were measured. (G) A model for SARS-CoV-2 N enhancing the interaction of M and PDK1. ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t-test. ns, non significant.