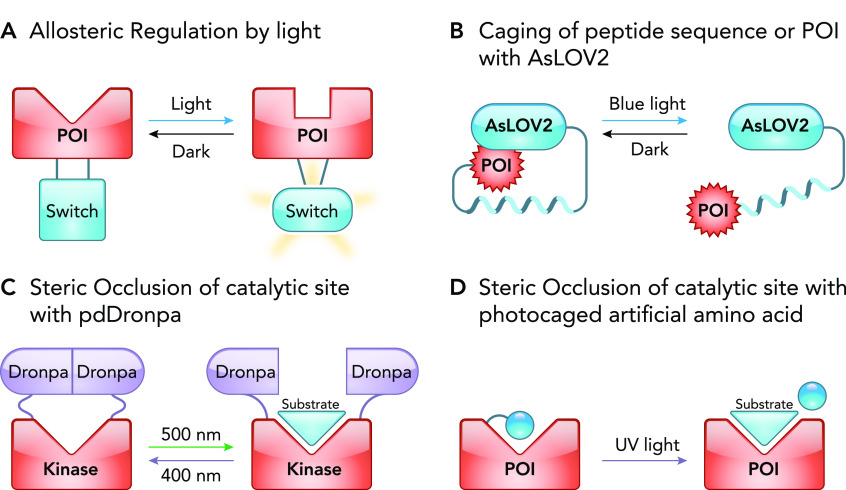
FIGURE 4.
Light-mediated regulation of proteins using allosteric and steric occlusion mechanisms
A: a light-sensitive allosteric switch regulates the structure of the catalytic site of a POI. B: schematic representation of photocaged signaling peptide or POI with AsLOV2. By fusing the POI to the Jα helix, AsLOV2 sterically occludes the POI in the dark. In the light, the Jα dissociates and becomes disordered, thus exposing and uncaging the POI. C: using the reversible dimerization property of pdDronpa, the active site of the POI is occluded by the pdDronpa dimer but exposed when pdDronpa dissociates. D: sterically occluding the active site by incorporating a photosensitive artificially caged amino acid near the substrate-binding pocket of a POI. Following exposure to light, the artificial amino acid is cleaved, resulting in the uncaging of the active site.