Figure 1 .
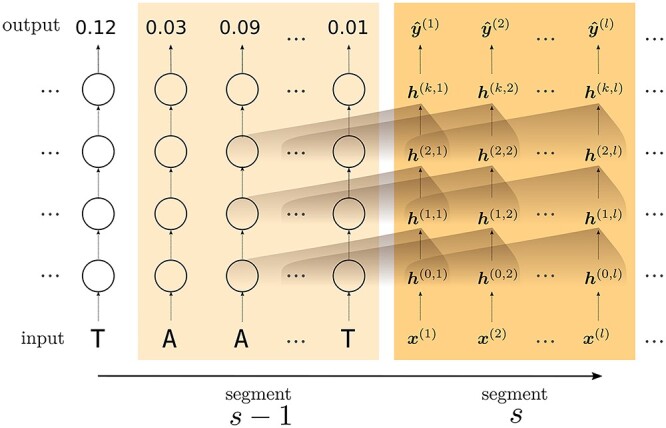
Illustration of the data flow within the transformer architecture. The full genome is processed in sequential segments 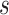 with length
with length 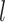 . First, the input nucleotide is transformed into a vector embedding
. First, the input nucleotide is transformed into a vector embedding 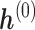 , after which it is processed by
, after which it is processed by 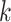 consecutive residual blocks (
consecutive residual blocks (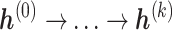 ). A set of fully connected layers transforms
). A set of fully connected layers transforms 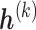 into a model output
into a model output 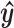 . For the calculation at each residual block, the upstream
. For the calculation at each residual block, the upstream 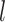 hidden states of the previous layer are applied (brown gradient). For example, the calculation of
hidden states of the previous layer are applied (brown gradient). For example, the calculation of 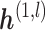 is based on the hidden states
is based on the hidden states 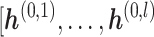 ]. Hidden states from the previous segment (
]. Hidden states from the previous segment ( ) are made accessible for the calculation of the hidden states in segment
) are made accessible for the calculation of the hidden states in segment 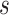 .
.
