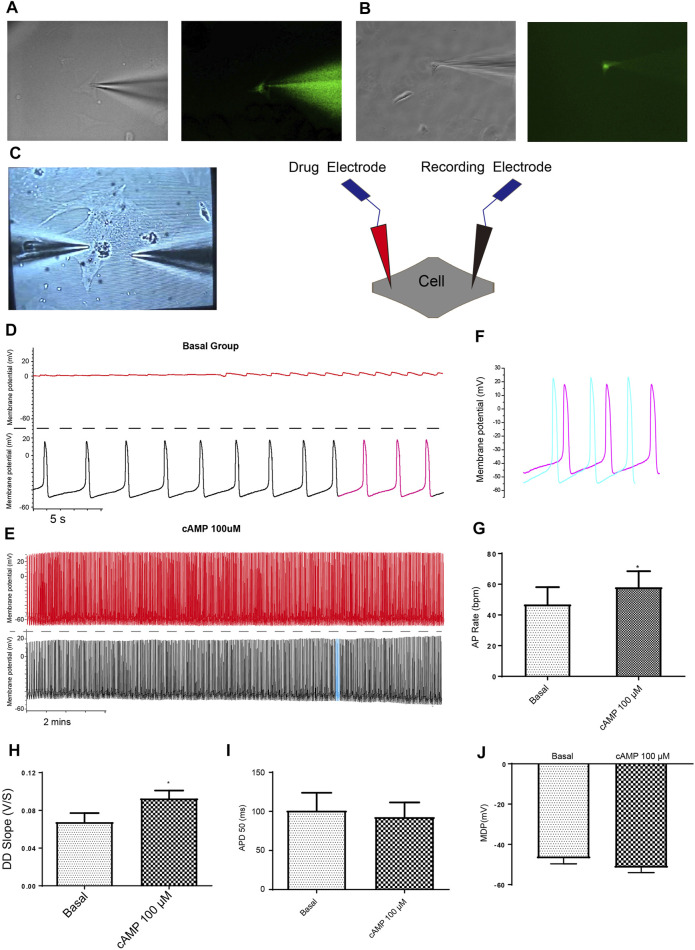
FIGURE 3.
Dual current patch clamp is an advantageous approach to investigate the effect of intracellular delivery of drugs on the APs of mESC-CMs reliably. (A) Ang II-FITC can be successfully delivered into mESC-CMs using the glass electrode as shown by the appearance of the green fluorescence signal inside the cell. (B) Calcium indicator Fluo-4-IM can be delivered into mESC-CMs without a leak from the glass electrode. (C) Bright view of a dual current patch clamp experiment of mESC-CMs (left panel). A schematic diagram on the dual patch clamp experimental configuration (right panel). In dual patch clamp, AP measurement will first be made using the “recording electrode” [as shown by black traces in (D) and (E); on the other hand, red traces in (D) and (E) represent recording in the “drug electrode”]. Before the membrane breakage by the “drug electrode”, the recording in the “recording electrode” serves as the “basal” level recording. After membrane breakage of the “drug electrode” and thereby the delivery of the drug to the intracellular environment, the AP measured in the “recording electrode” represents the effect of the drug. (D, E) cAMP was used as a positive control to show the utilization of dual patch clamp. (D) Representative trace showing the basal APs in mESC-CMs (before membrane breakage by the “drug electrode”). Upper panel represents recording in the “drug electrode” while the lower panel represents recording in the “recording electrode”. (E) Representative trace showing the APs after intracellular cAMP delivery (after membrane breakage by the “drug electrode”). Upper panel represents recording in the “drug electrode” while the lower panel represents recording in the “recording electrode”. (F) Traces labeled as pink in (D) (represents APs before intracellular cAMP delivery) and as blue in (E) (represents APs after intracellular cAMP delivery) are overlaid for comparison. (G–J) Summarized data on the (G) AP rate, (H) DD slope, (I) APD 50, and (J) MDP of APs upon treatment with cAMP (100 µM). cAMP increased the AP rate and the DD slope of APs. Values are mean ± SEM of 6–10 independent experiments. *p < 0.05 vs. control group.