Fig. 1.
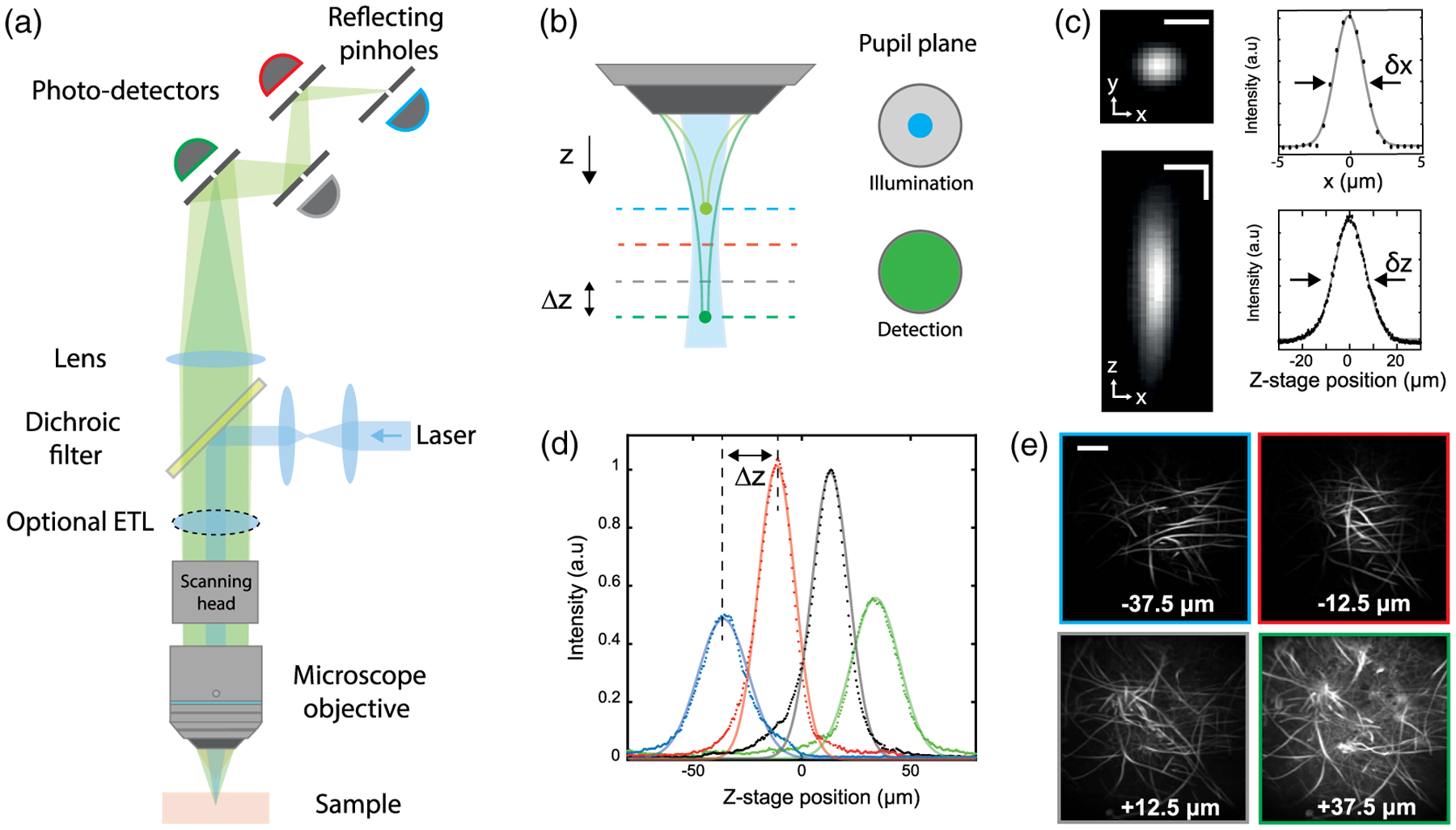
Multi-Z confocal microscopy. (a) Simplified schematic of the experimental setup. The multiplane detection unit comprises a series of axially distributed reflecting pinholes, each probing a different depth within the sample. (b) Axially extended illumination is obtained by underfilling the back aperture of the MO. The full NA of the MO is used for detection. (c) Transverse (xy) and axial (xz) PSF measured with a subdiffraction size bead, and associated x and z profiles. Horizontal scale bar, 5 μm. Vertical scale bar, 10 μm. (d) Bead signal recorded by each detection channel at different z positions of the stage. Continuous lines correspond to Lorentzian fits. (e) Different imaging planes simultaneously acquired of Aspergillus conidiophores. Scale bar, 200 μm.
