Figure 2.
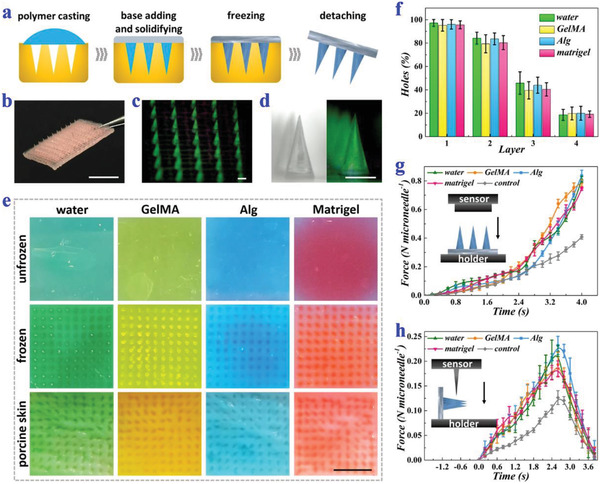
Fabrication, characterization, and mechanical strengths of ice microneedles. a) Schemes of the fabrication process of ice microneedles. b) Digital image of an ice microneedle patch. c) Fluorescence image of an ice microneedle array. d) Bright field and fluorescence field images of a single ice microneedle. e) Digital images of agarose after penetration of unfrozen water microneedles (dyed green), GelMA microneedles (dyed yellow), Alg microneedles (dyed blue), and Matrigel microneedles (dyed red); digital images of agarose after penetration of ice microneedles; digital images of porcine skins after penetration of ice microneedles. f) Penetration efficiency of ice microneedles into different layers of parafilm. The ice microneedles are made from water, GelMA, Alg, and Matrigel (n = 5 for each group). g) Compressive forces of four kinds of ice microneedles and PEGDA control ones (n = 3 for each group). h) Shear forces of four kinds of ice microneedles and PEGDA control ones (n = 3 for each group). Scale bars: 0.5 cm in (b,e) and 500 µm in (c,d).
