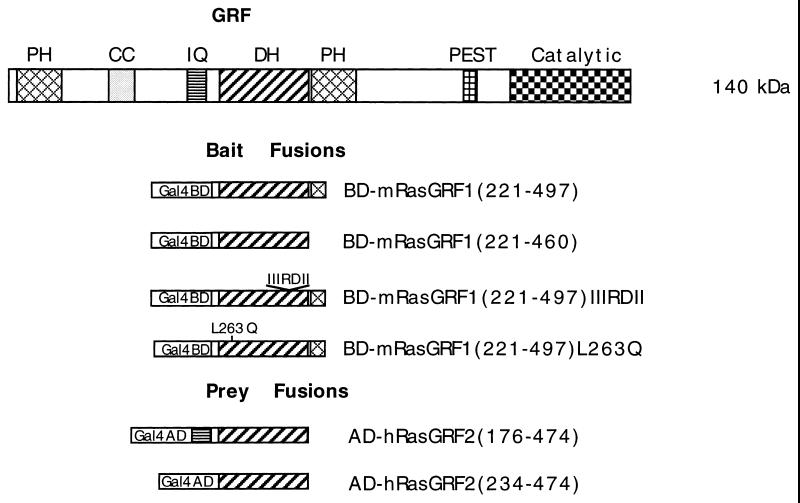
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the domain structure of GRF1 and of the baits and preys used in the two-hybrid interactions. The various abbreviations are as defined in the text; PEST is the protein instability motif, and Catalytic refers to the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange domain. In the bait fusions, Gal4BD represents the Gal4-binding domain (BD), while Gal4AD represents the Gal4 activation domain (AD) in the prey fusions. The numbers in parentheses refer to the corresponding amino acid residues of full-length mGRF1 encoded in the bait fusions and of full-length hGRF2 in the prey fusions. BD-mGRF1(221–497) is the starting bait fusion used in the two-hybrid screen. BD-mGRF1(221–460) lacks the PH domain codons in BD-mGRF1(221–497). BD-mGRF(221–497)IIIRDII harbors a cluster of substitutions in codons 394 to 400, while BD-mGRF1(221–497)L263Q contains a point mutation (see the text). AD-hGRF2(176–474) is the insert from clone pGAD10.56 obtained in the two-hybrid screen. In AD-hGRF2(234–474), the IQ motif codons have been deleted from the hGRF2 insert obtained in the two-hybrid screen.