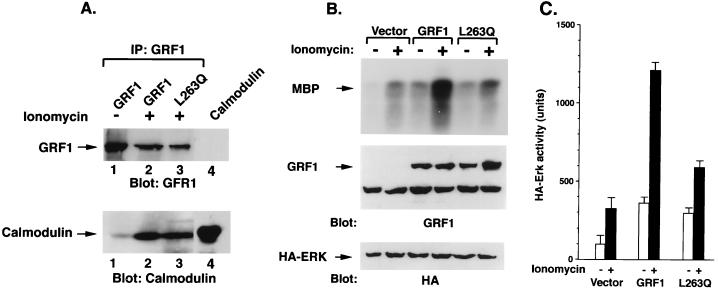
FIG. 6.
Calmodulin binding and ERK activity in 293T cells expressing wild-type GRF1 and L263Q mutant. (A) 293T cells were transiently transfected with wild-type GRF1 or the L263Q mutant, serum starved overnight, and either left untreated (−) or treated with ionomycin for 5 min (+). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with GRF1 antibodies and blotted with GRF1 antibodies (top portion of the panel) or with a calmodulin antibody (bottom portion of panel). Lane 4 contains only input calmodulin marker. (B) Basal and ionomycin-induced Erk activation in 293T cells transfected with GRF1. Cells were transiently transfected with vector, wild-type GRF1, or the L263Q mutant along with HA-ERK2, serum starved overnight, and either left untreated (−) or treated with ionomycin for 5 min (+). The exogenous ERK activity was determined as described in the text. The cells were processed and analyzed as described for panel A. (C) Quantitation of ERK activity. The amount of radioactivity present in phosphorylated MBP was quantitated with a phosphorimager. The activity of exogenous Erk was based on the mean of two experiments.