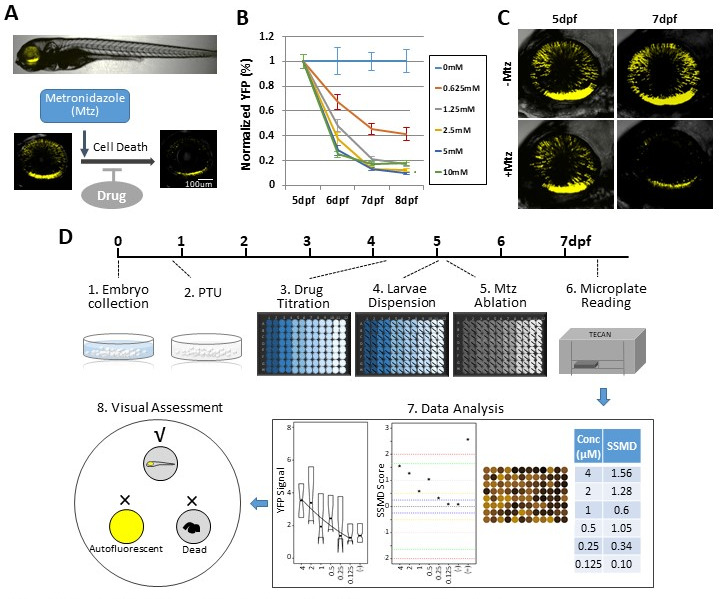
Figure 1. Zebrafish-inducible RP model and schematic of large-scale phenotypic screen.
(A–C) Prodrug (Metronidazole, Mtz) inducible ablation of rod photoreceptors in rho:YFP-NTR larvae. (A) In vivo confocal images of a rho:YFP-NTR larvae showing transgene expression specificity and whole retinas before and after Mtz-induced ablation of rod photoreceptors; schematic shows proposed neuroprotective effect of screened compounds. (B) Optimization of Mtz treatment regimen for large-scale screen: at five dpf, rho:YFP-NTR larvae were exposed to 10, 5, 2.5, 1.25, or 0.625 mM Mtz and YFP levels assessed daily by fluorescence microplate reader from 5 to 8 dpf (sample size: 56 larvae per group, two experimental repeats). The average YFP signal (±sem) for each Mtz treatment group is plotted as the percentage relative to non-ablated (0 mM Mtz) control signals per day. The 10, 5, and 2.5 mM Mtz-treated groups produced minimal YFP signal intensities (<20%) at 7 dpf (Supplementary file 1a; Figure 1B—source data 1). A 2.5 mM Mtz treatment over two days (5–7 dpf), the minimal Mtz concentration achieving maximal ablation, was therefore chosen for the large-scale primary screen. (C) Time series in vivo confocal images of representative non-ablated (-Mtz control, upper panel) and 2.5 mM Mtz-treated (+Mtz control, lower panel) retinas at 5 dpf (pre-Mtz) and 7 dpf (post-Mtz). By 7 dpf, only a limited number of YFP-positive cells are detectable in the +Mtz retina, mainly concentrated in a ventral band of high rod cell density. (D) Schematic of primary drug screening process: (1) At 0 dpf, large numbers of embryos were collected. (2) At 16 hpf, PTU was added to suppress melanization. (3) At 4 dpf, individual drugs were dispensed and titrated in 96-well plates using robotic liquid handlers; 16 wells per concentration (two columns) and six concentrations per drug. (4) At 5 dpf, the COPAS was used to dispense individual larvae into single wells of the drug titration 96-well plates. (5) After a 4 hr pre-exposure to drugs, larvae were treated with 2.5 mM Mtz to induce rod cell ablation. (6) At 7 dpf, YFP signals were quantified by fluorescence microplate reader assay. (7) Same day data analysis using a custom R code (https://github.com/mummlab/ARQiv2; Ding and Zhang, 2021) was used to plot signal to background ratios, SSMD plot, microplate heat map, and SSMD score table. (8) Drug plates producing SSMD scores of ≥1 were visually inspected using fluorescence stereomicroscopy to exclude autofluorescent and lethal compounds.