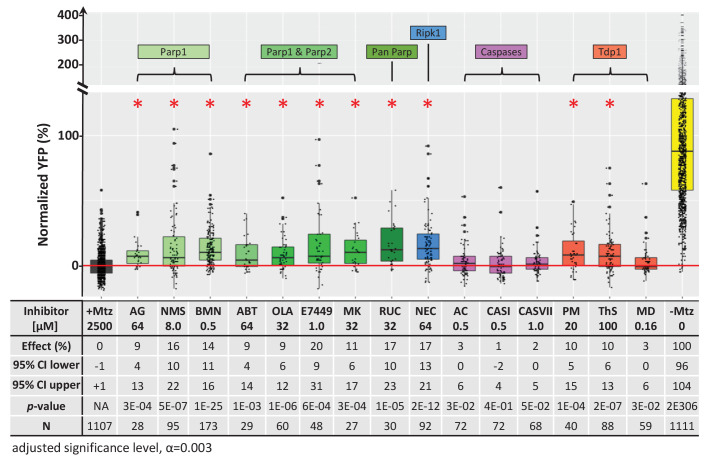
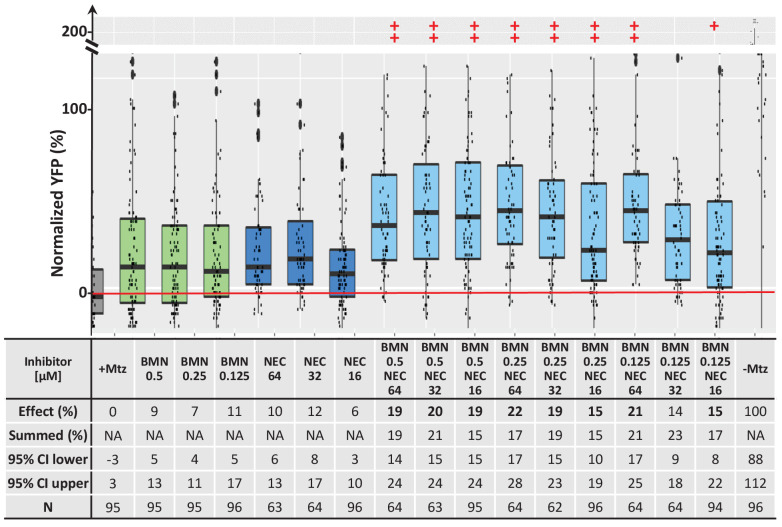
Figure 7. Chemical inhibitor analysis of NTR/Mtz-mediated rod cell death in zebrafish.
Box plots of rod cell survival effects of eight PARP inhibitors (green), a necroptosis inhibitor (blue), four apoptosis inhibitors (magenta), and three Tdp1 inhibitors (orange) in Mtz-treated rho:YFP-NTR zebrafish larvae (targets are listed above for each category). Assays performed as per confirmation tests (see Figure 2A) with all inhibitors tested across 10 concentrations using a twofold dilution series (see Methods for highest concentration tested per compound). Conditions resulting in a statistically significant increase in survival effects relative to +Mtz controls are marked with an asterisk. Survival effects (normalized YFP %), 95% confidence intervals, p-values, and sample sizes (N) for each condition are shown in the table below. Student’s t-test was used to calculate p-values for each condition relative non-ablated controls (0 mM Mtz). Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons resulted in an adjusted significance level of 0.003 (α=0.003). A minimum of two experimental repeats was performed for each condition (Figure 7—source data 1). No statistical differences in larval survival were observed for tested compounds relative to their respective +Mtz controls, except for PM (67%; Fisher’s exact test, p<0.05). Target abbreviations: Parp, Poly (ADP)-ribose polymerase; Ripk1, Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase (1); Tdp1, Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1; Mtz, metronidazole. Inhibitor abbreviations: AG, AG-14361; NMS, NMS-P118; BMN, talazoparib; ABT, veliparib; OLA, olaparib; MK, niraparib; RUC, rucaparib; NEC, necrostatin-1; AC, Ac-DEVD-CHO; CASI, caspase3/7 inhibitor I; CASVII, caspase three inhibitor VII; PM, paromomycin; ThS, thiostrepton; MD, methyl-3,4-dephostatin. Other abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; Mtz, Metronidazole.