Figure 11.
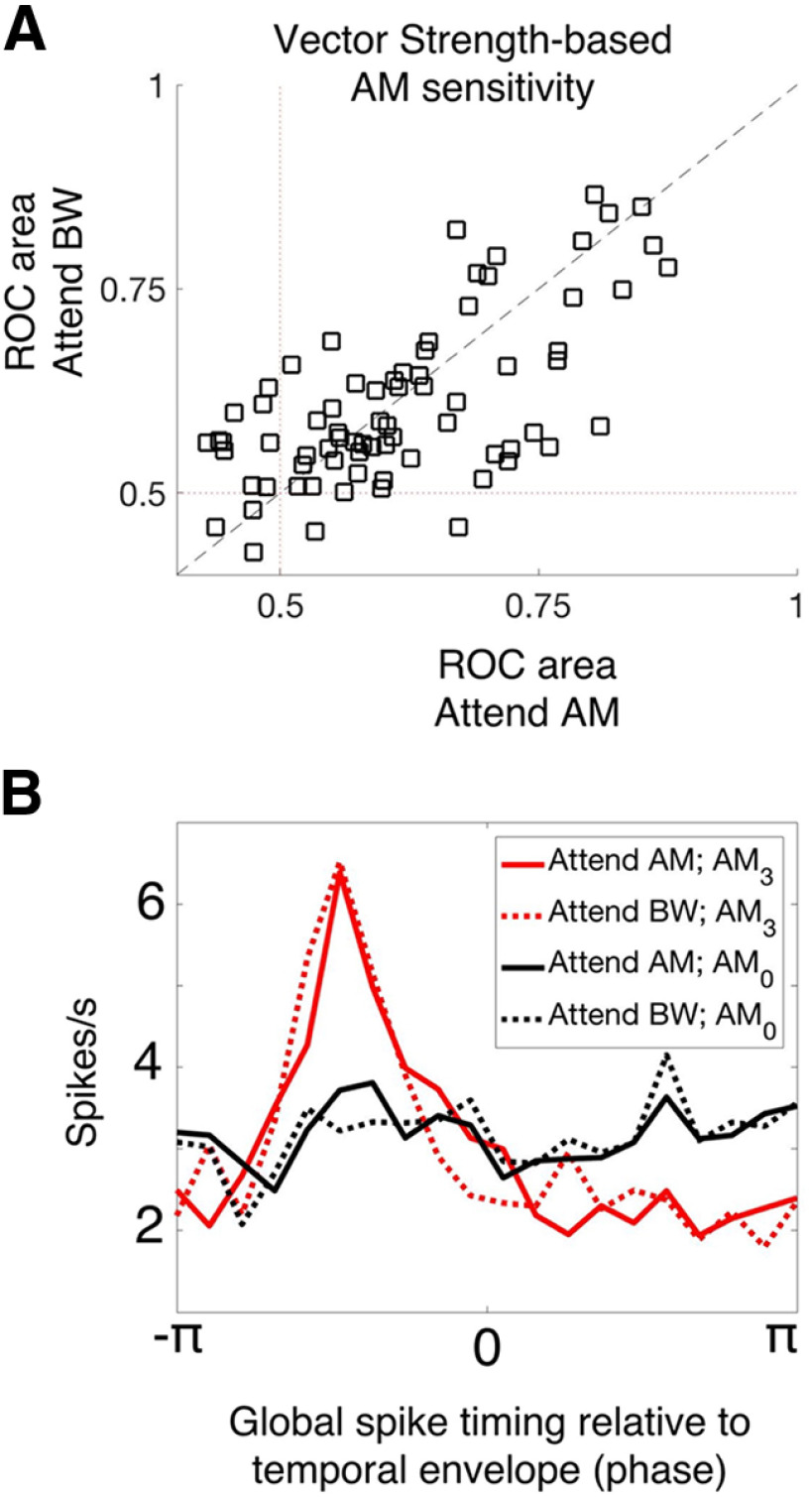
No evidence of attention-related changes in spike-timing-based sound encoding. A, We plot the vector strength-based neural sensitivity (ROC area) of each A1 neuron across attention conditions (attend AM, x-axis; attend BW, y-axis). There is no average difference in ROC area between conditions (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p = 0.8849). B, We analyzed the tendency for neurons to fire spikes in the same phase relative to the temporal modulation. Global spike timing in response to the fully temporally modulated stimulus (AM3, red) shows a prominent peak relative to the unmodulated stimulus (AM0, black), indicating that A1 neurons tend to fire synchronous spikes relative to temporal modulation. We observe no effect of attention on this property of A1 neurons (solid lines vs dashed lines). These results indicate a lack of attentional modulation on the response dynamics of A1 neurons.