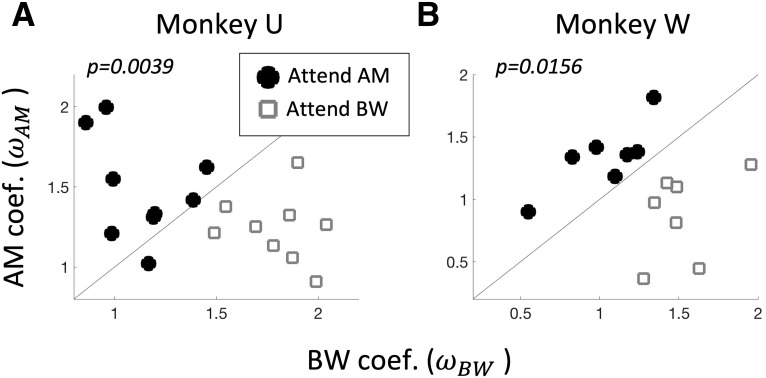
Figure 2.
Both monkeys perform the task. For each monkey (Monkey U in A and Monkey W in B), we show the behavioral coefficients (and ) calculated from Equation 1 across all sessions in which a recording was performed in A1. Open gray squares and filled black circles indicate the attention condition (attend BW and attend AM, respectively). Selective detection of the attended feature over the distractor feature is evident for both animals by higher values than values during attend AM and vice versa during attend BW [signed-rank test, p = 0.0039 (Monkey U), p = 0.0156 (Monkey W)].