Figure 2.
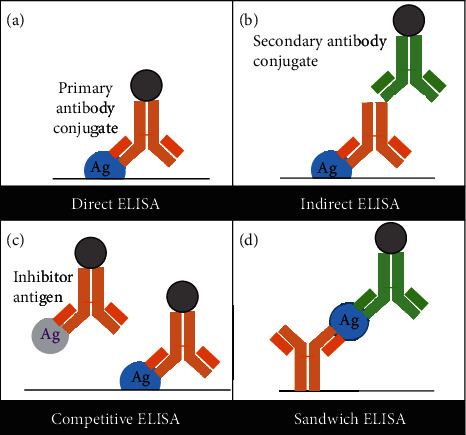
Types of ELISA. (a) Direct: an antigen is immobilized on the surface of a multiwell plate. A labeled primary antibody binds to the target antigen and is detected using an enzymatic substrate. (b) Indirect: an indirect ELISA consists of an unconjugated antibody binding to the target antigen, followed by a conjugated antibody. (c) Competitive: this assay is also known as an inhibition assay. The target antigen is precoated on a multiwell plate. An enzyme-labeled antibody is preincubated with the sample and may form antibody-antigen complexes with the inhibitor antigen before being added to the multiwell plate. The free antibody binds to the target antigen immobilized on the surface of a multiwell plate. A lower signal corresponds to a higher amount of antigen. (d) Sandwich: the sandwich “capture” assay is the most complex but provides sensitive and highly specific detection using two antibodies that preferably bind to two different epitopes. The antigen binds to the capture antibody and is detected using a second “detection” antibody. A labeled secondary antibody is then used to produce a measurable signal.
