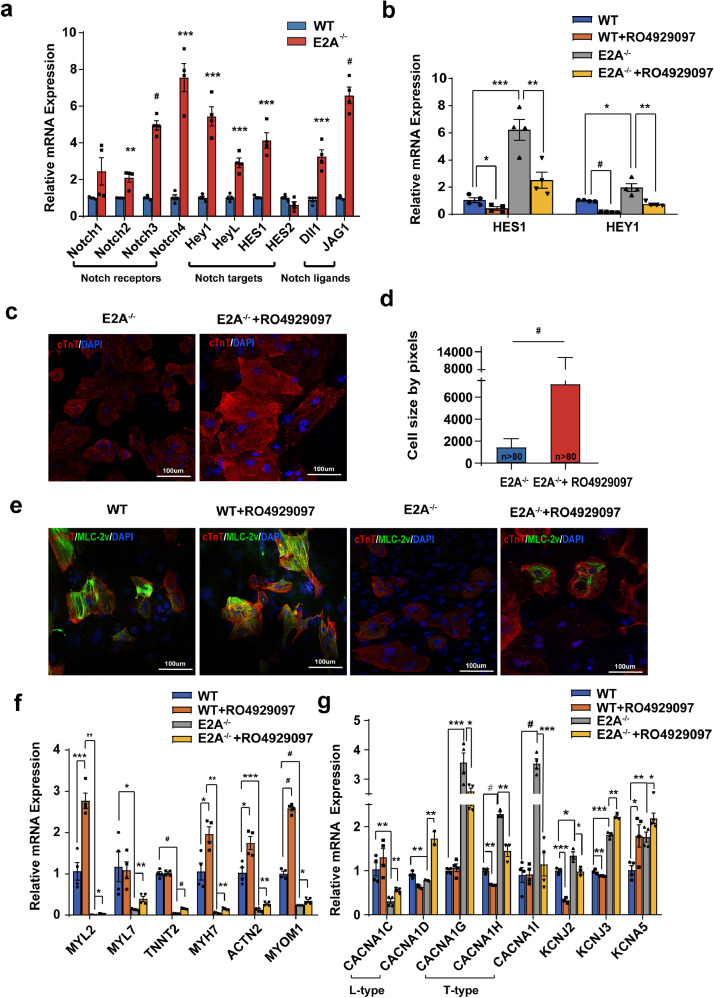
Fig. 6.
E2A partially relies on regulating the activity of NOTCH signal pathway for involving in CMs differentiation process and its inhibitor reversed the phenotypes of E2A knockout CMs.
(a) mRNA levels of representative NOTCH signal pathway genes after E2A knockout. Data were normalized to GAPDH level and presented as mean ± SEM. * P value < 0.05, ** P value < 0.01, *** P value < 0.01, # P value < 0.0001(Two-tailed Student's t-test). (b) Expression of NOTCH target genes HES1 and HEY1 in day30 CMs of WT and E2A−/- after treated with NOTCH inhibitor. Data were normalized to GAPDH level and presented as mean ± SEM. * P value < 0.05, ** P value < 0.01, *** P value < 0.01, # P value < 0.0001(ANOVA) (c) Cell areas of E2A−/- CMs increased after inhibition of NOTCH signal pathway. (d) Statistic of cell size of E2A−/- CMs after interfering NOTCH signaling. (e) Increased expression of cTnT and MLC-2v in E2A knockout CMs after treated with NOTCH inhibitor (RO4929097). All data were presented as mean ± SEM. # P value < 0.001(Two-tailed Student's t-test). (f) mRNA levels of structures genes were partially rescued in E2A−/- CMs after inhibition of NOTCH signal pathway. Data were normalized to GAPDH level and presented as mean ± SEM. * P value < 0.05, ** P value < 0.01, *** P value < 0.01, # P value < 0.0001(ANOVA). (g) mRNA expression of L-type calcium channels genes was increased, while which of T-type calcium channels and several other ion channels were decreased in E2A−/- CMs after treated with NOTCH inhibitor. All data were presented as mean ± SEM. * P value < 0.05, ** P value < 0.01, *** P value < 0.001, # P value < 0.001(ANOVA).