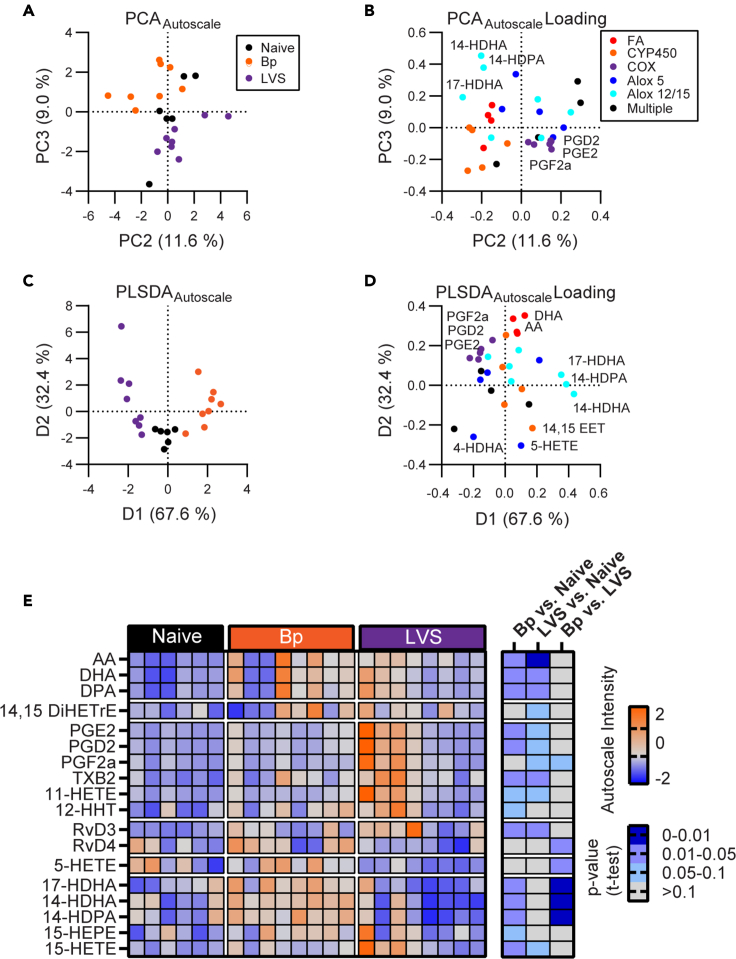
Figure 7.
Analysis of PUFA-derived immune lipid mediators indicates pathogen-specific LM profiles in the experienced lung
Lipid mediator (LM) profile was determined in naive, Bordetella pertussis (Bp; day 42 post-infection), and Francisella tularensis LVS (LVS; day 28 post-infection) experienced lungs.
(A) PCA separation of the autoscaled LM data set of the experienced lungs.
(B) Corresponding loading plot.
(C) PLSDA analysis of the autoscaled LM data set of the experienced lungs
(D) Corresponding loading plot. For loading plots, LMs are colored by their enzyme of origin.
(E) Heatmap of the autoscaled intensities of LM features that passed a 10% FDR cutoff for one of the three possible binary comparisons. Corresponding p values from the binary comparison are displayed at right. AA, arachidonic acid; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; DPA, docosapentaenoic acid; Rv(X), resolvin; HETE, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; HEPE, hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid; HDHA, hydroxydocosahexaenoic acid; HDPA, hydroxydocosapentaenoic acid; DiHETrE, dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid; HHT, hydroxyheptadecatrenoic acid; PG(X), prostaglandin; TxB2, Thromboxane B2. Data are composite of 2 independent experiments with n = 6 for naive, n = 8 for Bp and LVS in total.